
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 647-652.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140633
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
FENG Ming-Yan, TIAN Jian-Huan, LIU Yuan-Yuan, SHAN Zhong-Qiang
Received:2014-12-05
Revised:2015-02-27
Published:2015-06-04
Online:2015-05-22
About author:FENG Ming-Yan. E-mail: fmyxinya125@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
FENG Ming-Yan, TIAN Jian-Huan, LIU Yuan-Yuan, SHAN Zhong-Qiang. Effect of Silicon Anode Additives on Lithium Ion Batteries[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(6): 647-652.
| Samples | AB | SuperP | VulcanXC-72 | BP2000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 BET surface area /(m2·g-1) | 54.55 | 75.80 | 212.30 | 890.60 |
| Average particle size /nm | 37.61 | 39.24 | 18.96 | 18.26 |
| Electrical resistivity /(Ω·cm) | 0.3995 | 0.2802 | 0.8620 | 0.7336 |
| Electrical resistivity of silicon electrodes /(Ω·cm) | 2.0303 | 1.7726 | 5.5808 | 5.3292 |
Table 1 Surface area, average particle size, electrical conductivity of different conductive additives and electrical resistivity of electrodes with different conductive additives
| Samples | AB | SuperP | VulcanXC-72 | BP2000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 BET surface area /(m2·g-1) | 54.55 | 75.80 | 212.30 | 890.60 |
| Average particle size /nm | 37.61 | 39.24 | 18.96 | 18.26 |
| Electrical resistivity /(Ω·cm) | 0.3995 | 0.2802 | 0.8620 | 0.7336 |
| Electrical resistivity of silicon electrodes /(Ω·cm) | 2.0303 | 1.7726 | 5.5808 | 5.3292 |
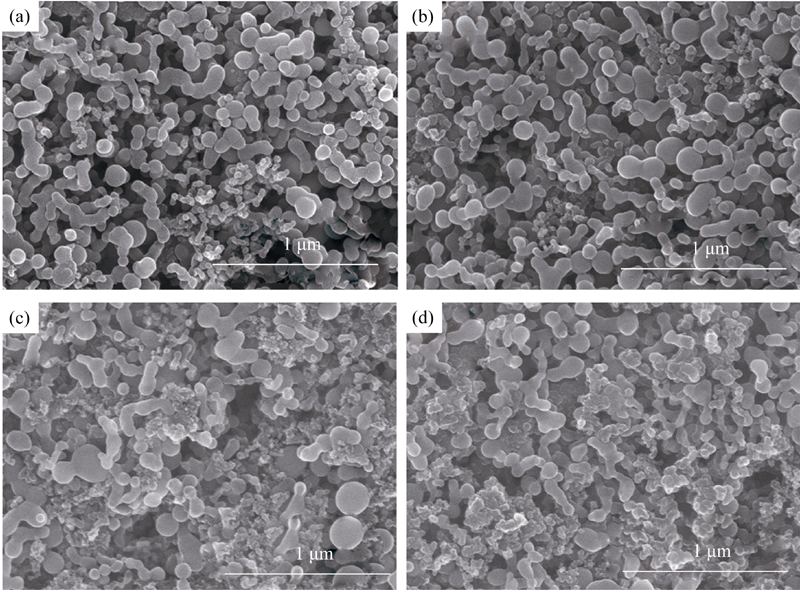
Fig. 1 SEM images of silicon electrodes containing 15wt% binder CMC with different conductive additives (a) Acetylene black; (b) SuperP; (c) BP2000; (d) VulcanXC-72
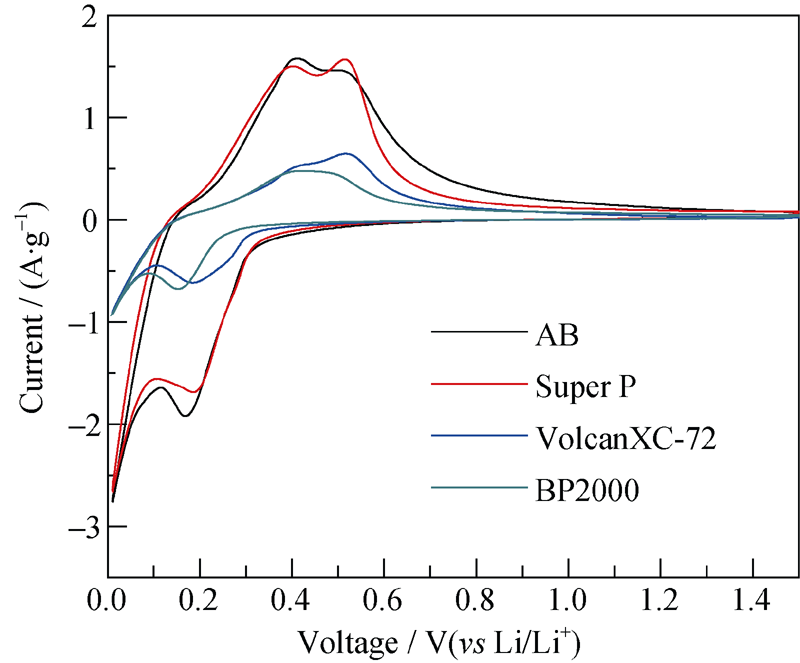
Fig. 2 Cyclic voltammogram curves of silicon electrodes containing 15wt% binder CMC with different conductive additives at potential scanning rate of 0.1 mV/s
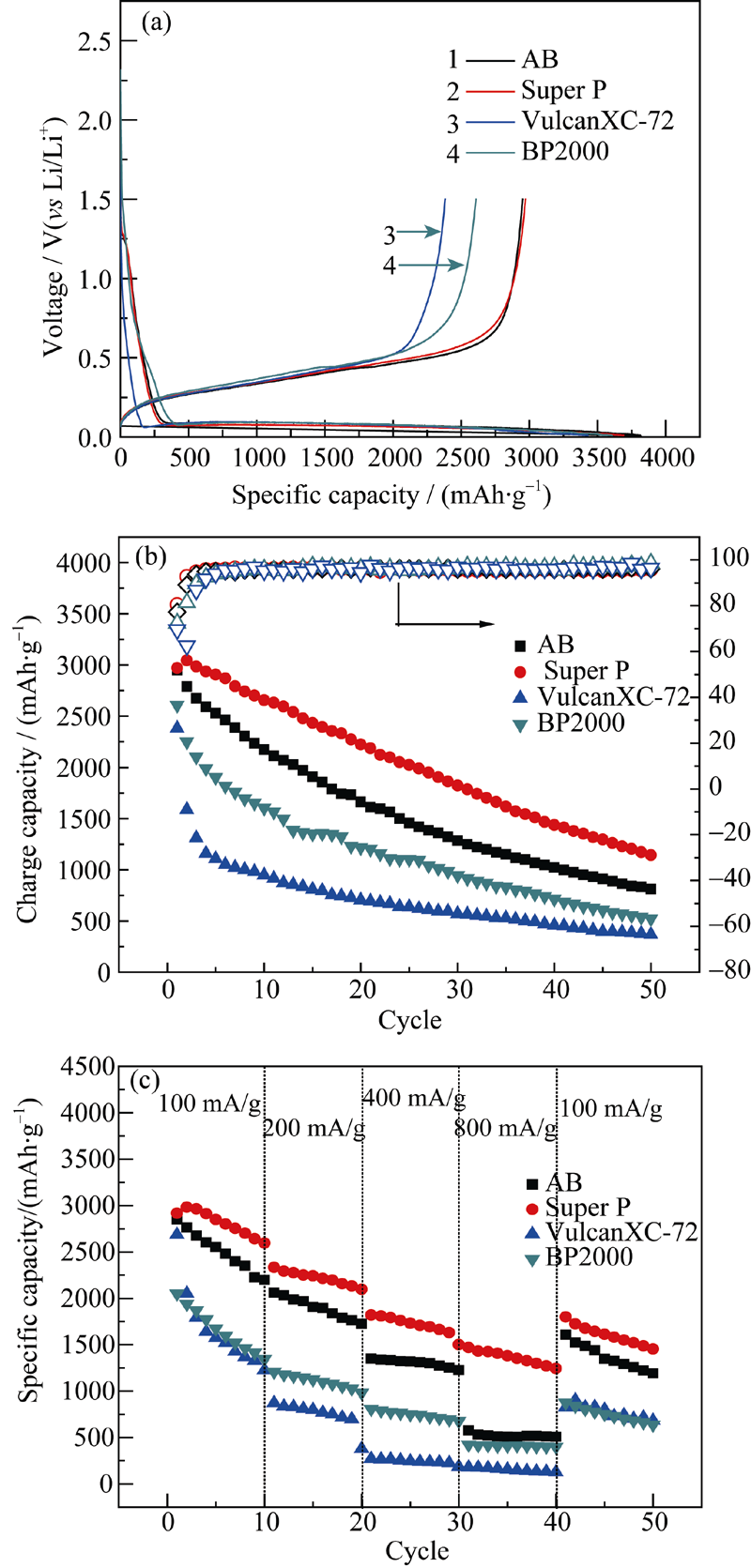
Fig. 3 First charge-discharge curves (a), cycling performance at 200 mA/g (b) and rate performance (c) of silicon electrodes containing 15wt% binder CMC with different conductive additives
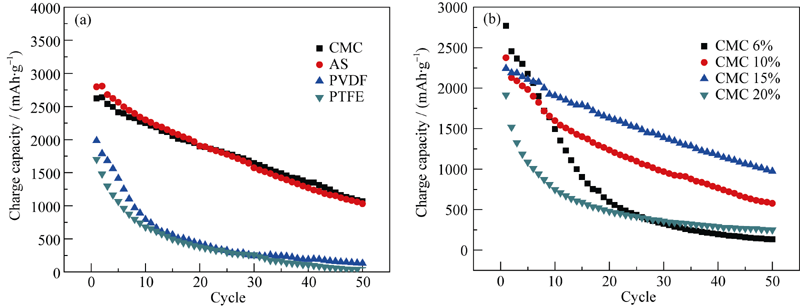
Fig. 5 Influence of binder on the cycle performance of silicon electrodes containing 15wt% conductive SuperP (a) Different binders, (b) Different CMC content
| [1] | PENG P, LIU Y, WEN Z Y.Electrochemical performance of silicon/carbon/graphite composite anode for lithium ion batteries. J. Inorg. Mater., 2013, 28(11): 1195-1199. |
| [2] | KIM H, HAN B, CHOO J, et al.Three-dimensional porous silicon particles for use in high-performance lithium secondary batteries. Angew. Chem., 2008, 120(52): 10305-10308. |
| [3] | KIM H, SEO M, PARK M H, et al.A critical size of silicon nano-anodes for lithium rechargeable batteries.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, 2010, 49(12): 2146-2149. |
| [4] | SONG T, XIA J, LEE J H, et al.Arrays of sealed silicon nanotubes as anodes for lithium ion batteries. Nano Lett., 2010, 10(5): 1710-1716. |
| [5] | ZHANG P C, YANG X L, YU D X, et al.Synthesis of silicon/carbon composite anode prepared by in-situ carbothermal reduction for lithium ion batteries.J. Inorg. Chem., 2011, 27(5): 898-902. |
| [6] | XIA F, KIM S B, CHENG H, et al.Facile synthesis of free-standing silicon membranes with three-dimensional nanoarchitecture for anodes of lithium ion batteries.Nano Lett., 2013, 13(7): 3340-3346. |
| [7] | HU Y S, DEMIR C R, TITIRICI M M, et al.Superior storage performance of a Si@SiOx/C nanocomposite as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, 2008, 47(9): 1645-1649. |
| [8] | HWA Y, KIM W S, HONG S H, et al.High capacity and rate capability of core-shell structured nano-Si/C anode for Li-ion batteries.Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 71: 201-205. |
| [9] | ZHU Y, LIU W, ZHANG X, et al.Directing silicon-graphene self-assembly as a core/shell anode for high-performance lithium-ion batteries.Langmuir, 2013, 29(2): 744-749. |
| [10] | LIU W R, GUO Z Z, YONG W S, et al.Effect of electrode structure on performance of Si anode in Li-ion batteries: Si particle size and conductive additive. J. Power Sources, 2005, 140(1): 139-144. |
| [11] | DING N, XU J, YAO Y, et al.Improvement of cyclability of Si as anode for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources, 2009, 192(2): 644-651. |
| [12] | WANG M S, FAN L Z, HUANG M, et al.Conversion of diatomite to porous Si/C composites as promising anode materials for lithium- ion batteries. J. Power Sources, 2012, 219: 29-35. |
| [13] | REN J G, WU Q H, HONG G, et al.Silicon-graphene composite anodes for high-energy lithium batteries.Energy Technol., 2013, 1(1): 77-84. |
| [14] | LIU P, SRIDHAR N, ZHANG Y W.Lithiation-induced tensile stress and surface cracking in silicon thin film anode for rechargeable lithium battery.J. Appl. Phys., 2012, 112(9): 093507. |
| [15] | KOVALENKO I, ZDYRKO B, MAGASINSKI A, et al.A major constituent of brown algae for use in high-capacity Li-ion batteries.Science, 2011, 334(6052): 75-79. |
| [16] | KOO B, KIM H, CHO Y, et al.A highly cross-linked polymeric binder for high-performance silicon negative electrodes in lithium ion batteries.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, 2012, 51(35): 8762-8767. |
| [17] | YUE L, ZHANG L, ZHONG H.Carboxymethyl chitosan: a new water soluble binder for Si anode of Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources, 2014, 247: 327-331. |
| [1] | CAI Ya-Ling, LI Ya-Fei, WANG Zeng-Mei, ZHANG Yao, CHEN Jian, GUO Xin-Li. CTAB-assisted Synthesis of MoS2/C Nano-flowers with Improved Electrochemical Performances for Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(12): 1289-1294. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xu, WANG Yu, LI Yue, YANG Meng, ZHAO Xiang-Yu, MA Li-Qun. Effect of Nickle Substitution on the Performance of Lithium Ion Battery Material LiMnTiO4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(7): 739-744. |
| [3] | TIAN Li-Yuan, YAO Zhi-Heng, LI Feng, WANG Yong-Long, YE Shi-Hai. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Red Phosphorus/Carbon Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(6): 653-661. |
| [4] |
LI Yun-Jiao, XU Hu, KONG Long, LI Hua-Cheng, LI Chun-Xia, ZHANG Xian-Zhen, HAN Qiang.
Synthesis and Electrochemical Characterizations of Co-doped Lithium Manganese Oxide Spinel Li1.035Mn1.965O4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(6): 661-666. |
| [5] | YU Xiao-Lei, YANG Jun, FENG Xue-Jiao, GAO Peng-Fei, WANG Jiu-Lin, NULI Yan-Na. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of Porous Silicon/Carbon Composite as Negative Electrode Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(9): 937-942. |
| [6] | WANG Yan-Ming, WANG Fei, WANG Guang-Jian. Sol-Gel Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of LiMnPO4/C Cathode Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(4): 415-419. |
| [7] | ZHENG Yue-Lei, CHEN Ren-Jie, WU Feng, LI Li. Progress of Research on the Conductive Mechanism of the Glassy Electrolytes in Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(11): 1172-1180. |
| [8] | PENG Peng, LIU Yu, WEN Zhao-Yin. Electrochemical Performance of Silicon/Carbon/Graphite Composite Anode for Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(11): 1195-1199. |
| [9] | MOU Fei, YANG Xue-Lin, DAI Zhong-Xu, ZHANG Lu-Lu, WEN Zhao-Yin. Effect of Sintering-method on Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4/C Cathode Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(8): 838-842. |
| [10] | DENG Fei, ZENG Xie-Rong, ZOU Ji-Zhao, LI Xiao-Hua. Effects of Preparation Temperature on Pyrolytic Carbon Coated LiFePO4/Vapor-grown Carbon Fiber (PCLFP/VGCF) Composite Cathode Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(11): 1141-1146. |
| [11] | JIA Wei, XU Mao-Wen, BAO Shu-Juan, JIA Dian-Zeng. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Porous TiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(12): 1335-1339. |
| [12] | SUN Ke,LU Hai-Wei,LI Da,ZENG Wei,LI Yue-Sheng,FU Zheng-Wen. Electrospun Manganese Oxides Nanofibers Electrode for Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(2): 357-360. |
| [13] | ZHOU Xin,ZHAO Xin-Bing,YU Hong-Ming,HU Jie-Zi. Electrochemical Properties of F-doped LiFePO4/C Prepared by Solid-state Synthesis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(3): 587-591. |
| [14] | LI Xin-Lu,KANG Fei-Yu,BAI Xin-De,SHEN Wan-Ci. Microstructure and Electrochemical Properties of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 Coated with Al2O3 Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(6): 1037-1040. |
| [15] | WEN Zhong-Sheng,WANG Ke,XIE Jing-Ying. Interface Formed on High Capacity Silicon Anode for Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(3): 437-441. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||