
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 1313-1319.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140115
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LU Jin-Rong, ZHOU Yang, LI Hai-Yan, ZHENG Yong, LI Shi-Bo, HUANG Zhen-Ying
Received:2014-03-11
Revised:2014-05-15
Published:2014-12-20
Online:2014-11-20
About author:LU Jin-Rong. E-mail: ljr012937@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LU Jin-Rong, ZHOU Yang, LI Hai-Yan, ZHENG Yong, LI Shi-Bo, HUANG Zhen-Ying. Wettability and Wetting Process in Cu/Ti3SiC2 System[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(12): 1313-1319.
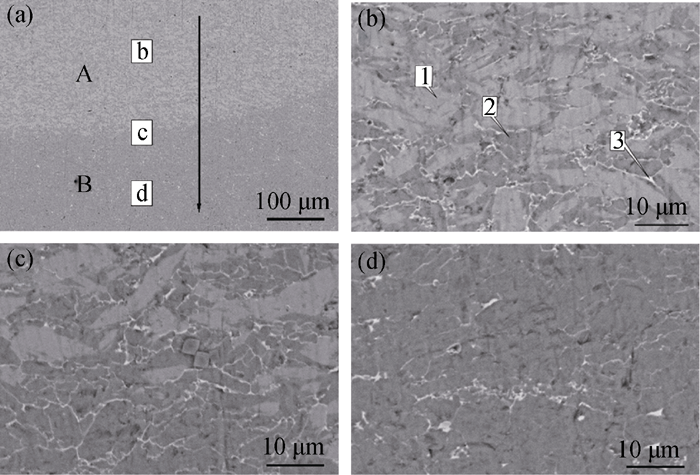
Fig. 5 Microstructure of the longitudinal section of Ti3SiC2 wetted by Cu at 1270℃ (a) Microstructure; (b) Enlarged image of the rectangular area marked in layer A showing the positions for EDS spot analysis; (c) Enlarged image of the rectangular area marked in the interfacial area between layer A and layer B; (d) Enlarged image of the rectangular area marked in layer B
| Atomic fraction / % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Si | Ti | Cu | |
| 1 | 41.87 | 8.05 | 42.09 | 7.99 |
| 2 | 46.31 | 12.04 | 41.65 | 0 |
| 3 | 45.36 | 7.27 | 25.67 | 21.70 |
Table 1 EDS spot analyses in the interfacial area of Cu/Ti3SiC2 system as shown in Fig. 5(b)
| Atomic fraction / % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Si | Ti | Cu | |
| 1 | 41.87 | 8.05 | 42.09 | 7.99 |
| 2 | 46.31 | 12.04 | 41.65 | 0 |
| 3 | 45.36 | 7.27 | 25.67 | 21.70 |
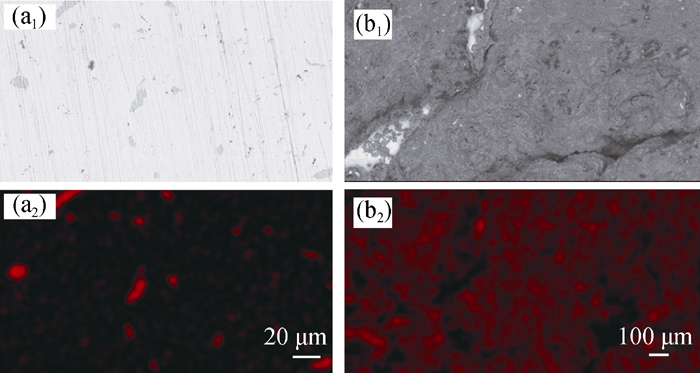
Fig. 9 Morphologies and element distributions of Ti in the base area of Cu-1wt%Ti alloy block (a1) Morphology before wetting experiment; (a2) Distribution of Ti in (a1); (b1) Morphology after wetting experiment; (b2) Distribution of Ti in (b1)
| [1] | LI Y, LIU N, ZHANG X B, et al.Effect of carbon content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ultra-fine grade (Ti,W)(C,N)-Co cermets. J. Mater. Process Tech., 2008, 206(1/2/3): 365-373. |
| [2] | AZADMEHR A, TAHERI-NASSAJ E. An in situ (W,Ti)C-Ni composite fabricated by SHS method. J. Non-cryst. Solids, 2008, 354(27): 3225-3234. |
| [3] | WANG L D, XUE Z W, QIAO Y J, et al.Anisotropic thermal expansion behaviors of copper matrix in β-eucryptite/copper composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2012, 177(11): 873-876. |
| [4] | LIU De-Bao, CUI Chun-Xiang.Fabrication and electrical conductivity property of copper-matrix composites reinforced with different ceramics particles. Journal of Functional Materials, 2004, 35: 1064-1067 |
| [5] | LI H, PENG L M, GONG M, et al.Preparation and characte rization of Ti3SiC2 powder. Ceram. Int., 2004, 30(8): 2289-2294. |
| [6] | ZHANG Z F, SUN Z M, HASHIMOTO H, et al.Effects of sintering temperature and Si content on the purity of Ti3SiC2 synthesized from Ti/Si/TiC powders. J. Alloys Compd., 2003, 352(1/2): 283-289. |
| [7] | GAO Run-Feng, MEI Bing-Chu, ZHU Jiao-Qun, et al.Research on new material for pantograph slide plates Cu/Ti3SiC2. Rare Metals Letters, 2005, 24(11):16-20. |
| [8] | GAO H P, ZHANG J, LI F Z, et al.Surface strengthening of Ti3SiC2 through magnetron sputtering Cu and subsequent annealing. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 28(10): 2099-2107. |
| [9] | SUN JIAN-JUN, ZHOU YANG, LU JIN-RONG, et al. Preparation and properties of Ti3SiC2/Cu composites. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy, 2011, 16(4):587-590. |
| [10] | LU J R, ZHOU Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Effects of sintering process on the properties of Ti3SiC2/Cu composite. Key Engineering Materials, 2012, 512-515:377-381. |
| [11] | YANG SHU-XIA, MEI BING-CHU, ZHOU WEI-BING, et al. Study on the carbon fiber reinforced Cu-Ti3SiC2 composite. Rare Metals Letters, 2008, 27(9):39-42. |
| [12] | CHEN JIAN, GU MING-YUAN, PAN FU-SHENG. Work of adhesion for reactive metal/ceramic systems. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2003, 20(3):85-88. |
| [13] | CHEN MING-HAI, LIU NING, XU YU-DONG. Development of research on the wettability of metal on ceramics. Cemented Carbide, 2002, 19(4):199-205. |
| [14] | LANDRY K, KALOGEROPOULOU S, EUSTATHOPOULOS N.Wettability of carbon by aluminum and aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. and Eng. A, 1998, 254(1/2):99-111. |
| [15] | EUSTATHOPOULOS N.Dynamics of wetting in reactive metal/ ceramic systems. Acta Mater., 1998, 46(7): 2319-2327. |
| [16] | ZARRINFAR N, KENNEDY A R, SHIPWAY P H.Reaction synthesis of Cu-TiCx master-alloys for the production of copper- based composites. Scripta Mater., 2004, 50(7):949-952. |
| [17] | KOOI B J, POPPEN R J, CARVALHO N J M. Ti3SiC2: a damage tolerant ceramic studied with nano-indentations and transmission electron microscopy. Acta Mater., 2003, 51(10): 2859-2872. |
| [18] | CHEN KANG-HUA, BAO CONG-XI, LIU HONG-WEI. Review of the study on the wettability of metal-ceramic. Materials Science and Engineering, 1997, 11(2):1-5. |
| [1] | SHANGGUAN Li, NIE Xiaoshuang, YE Kuicai, CUI Yuanyuan, QIAO Yuqin. Effects of Surface Wettability of Titanium Oxide Coatings on Osteoimmunomodulatory Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1457-1565. |
| [2] | DING Jianxiang,HUANG Peiyan,ZHA Yuhui,WANG Dandan,ZHANG Peigen,TIAN Wubian,SUN Zhengming. High-purity Ti2AlC Powder: Preparation and Application in Ag-based Electrical Contact Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(6): 729-734. |
| [3] | LI Dong, LEI Chao, LAI Hua, LIU Xiao-Lin, YAO Wen-Li, LIANG Tong-Xiang, ZHONG Sheng-Wen. Recent Advancements in Interface between Cathode and Garnet Solid Electrolyte for All Solid State Li-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(7): 694-702. |
| [4] | LIANG Yu, LIANG Ling-Yan, WU Wei-Hua, PEI Yu, YAO Zhi-Qiang, CAO Hong-Tao. Microfluidic-method-processed p-type NiOx Thin-film Transistors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(1): 79-84. |
| [5] | ZHANG Hao, GAO Peng-Yue, CHEN Guang-Yao, LI Ming-Yang, LU Xiong-Gang, LI Chong-He. Microstructure Evolution and Mechanism of Al2O3/BaZrO3 Double Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 819-824. |
| [6] | ZHANG Li-Li, LI Ke,YU Chen-Chen, ZHANG Yu-Wen, WU Cheng-Zhang, DING Wei-Zhong. Wetting Properties and Interface Reaction Mechanism of Ag-Cu Brazes on Dual-phase Membrane Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(6): 607-612. |
| [7] | CHEN Fan, SHI Kai-Cheng, SUN Shi-Yang, ZHAO Bo-Wen, SHANG Hai-Long, LI Ge-Yang. Direct Brazing of Al/Al2O3 without Wettability of Molten Metal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(6): 602-606. |
| [8] | LU Yuan, LI Jing-Long, YANG Jian-Feng, LI Peng. Effects of Heat-treatment Temperature on Properties of Co-continuous β-Si3N4 Reinforced Al Matrix Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 277-281. |
| [9] | WANG He-Yun, LIU Qian, ZHOU Yao, ZHOU Zhen-Zhen, LIU Guang-Hui. Preparation and Properties of Carbon Fiber/Si3N4 Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(9): 1003-1008. |
| [10] | LU You-Jun, WANG Yan-Min, PAN Zhi-Dong, HUANG Zhen-Kun, WU Lan-Er. Effect of Carbon Nanoparticle Content on Machinability and Wettability of Carbon/Silicon Carbide Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(4): 429-432. |
| [11] | ZHANG Qiang, JIANG Long-Tao, WU Gao-Hui. Fabrication of Oxidized SiC Particles Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composite by Pressureless Infiltration Technique [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(4): 353-357. |
| [12] | HUANG Lin, NING Cong-Qin, DING Dong-Yan, BAI Shuo, QIN Rui, LI Ming, MAO Da-Li. Wettability and In Vitro Bioactivity of Doped TiO2 Nanotubes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(7): 775-779. |
| [13] | LI Jia-Ke,LIU Lei,LIU Yi-Chun,ZHANG Wen-Long,HU Wen-Bin. Preparation of Ti-Si Eutectic Brazes and its Weldability to SiC [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(1): 204-208. |
| [14] | LI Da,ZHANG Yue-Li,XIAO Wen-Jia,YANG Yang-Yi,HE Zhen-Hui. Fabrication and Investigation of Superhydrophobic-Hydrophilic CaBi4Ti4O15 Coatings [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(4): 745-748. |
| [15] | YANG Jing,CHEN Jie-Rong,YU Rong. Surface Wettability and Vapour Stability of Silica Membranes Modified by Sol-Gel Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(4): 739-744. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||