无机材料学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 221-228.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170394 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20170394
李永生, 陈玲
收稿日期:2017-08-14
修回日期:2017-10-31
出版日期:2018-02-26
网络出版日期:2018-01-26
作者简介:李永生(1972),男,教授.E-mail:ysli@ecust.edu.cn
LI Yong-Sheng, CHEN Ling
Received:2017-08-14
Revised:2017-10-31
Published:2018-02-26
Online:2018-01-26
摘要:
随着纳米催化剂的不断发展, 基于纳米金的多功能复合材料以其高效的催化性能而受到广泛关注。本研究采用简单可控的原位还原法, 制备了一种粒径均一、分散性良好、可快速磁分离且具有高催化活性与催化稳定性的磁性四氧化三铁-金纳米复合颗粒。首先用有机硅源-巯丙基三乙氧基硅烷(MPTES)水解得到的有机硅层来包覆粒径约100 nm的亲水四氧化三铁(Fe3O4)纳米颗粒, 再通过有机硅层表面的巯基来锚定原位还原生成的尺寸可控的金纳米颗粒(2 nm或6 nm), 得到内核为四氧化三铁、壳层为金纳米颗粒均匀修饰有机硅层的磁性氧化硅复合颗粒。利用透射电子显微镜(TEM)、动态光散射仪(DLS)和振动样品磁强计(VSM)等对所合成材料进行系统表征, 结果表明: 合成的磁性氧化硅复合颗粒核壳结构明显, 分散性良好, 粒径约为150 nm; 饱和磁强度为32.1 A•m2/kg, 具有良好的超顺磁特性。将其应用于4-硝基苯酚的催化还原, 转化频率(TOF)值高达70 s-1, 远高于文献报道值, 五次循环反应后的转化率依然高达98%, 证实其具备高催化活性及良好的循环催化性能。
中图分类号:
李永生, 陈玲. 可控制备磁性四氧化三铁-金纳米复合颗粒及其催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(2): 221-228.
LI Yong-Sheng, CHEN Ling. Controlled Synthesis of Gold-based Magnetic Nanocomposites and Their Catalytic Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(2): 221-228.
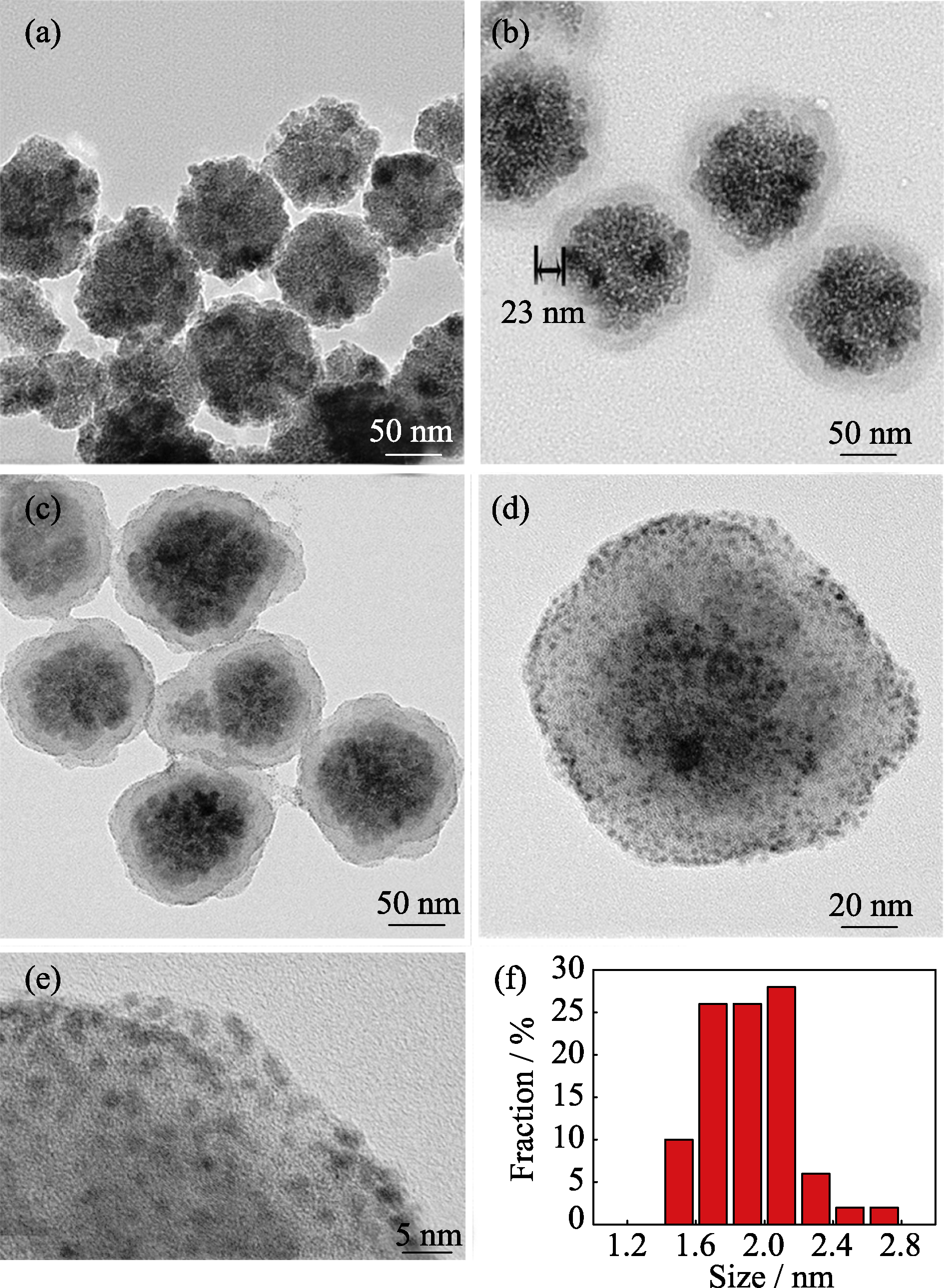
图2 (a) Fe3O4, (b) MCN, (c~e) MCN-Au (2 nm)的透射电镜照片; (f) MCN-Au (2 nm)上负载Au NPs的粒径分布
Fig. 2 TEM images of (a) Fe3O4 particles, (b) MCN nanospheres, (c-e) MCN-Au (2 nm); (f) Size distribution of Au NPs on MCN-Au (2 nm)
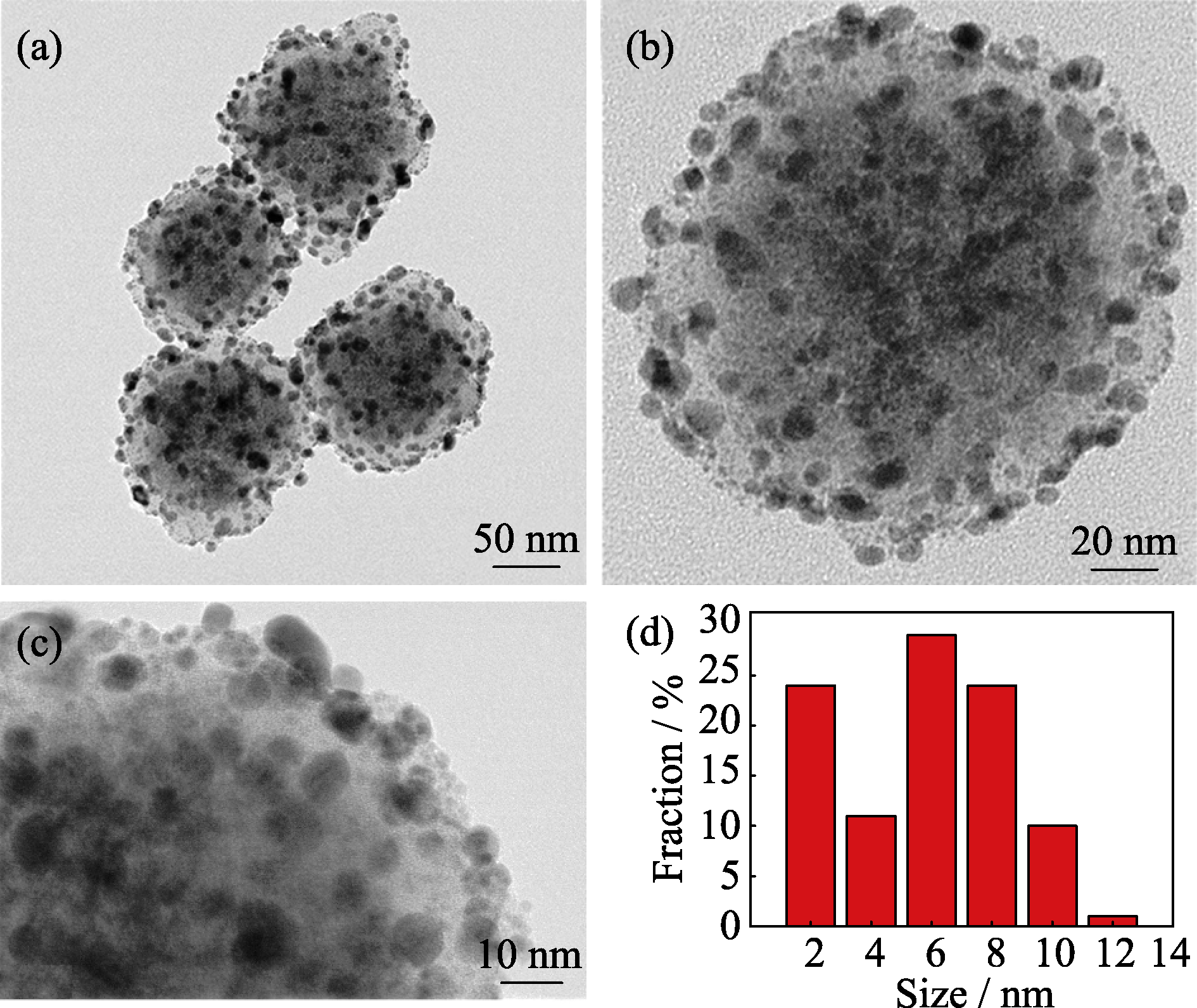
图3 (a~c) MCN-Au (6 nm)的透射电镜照片; (d) MCN-Au (6 nm)上负载的Au NPs的粒径分布
Fig. 3 TEM images of (a-c) MCN-Au (6 nm); (d) Diameter distribution of Au NPs on MCN-Au (6 nm)
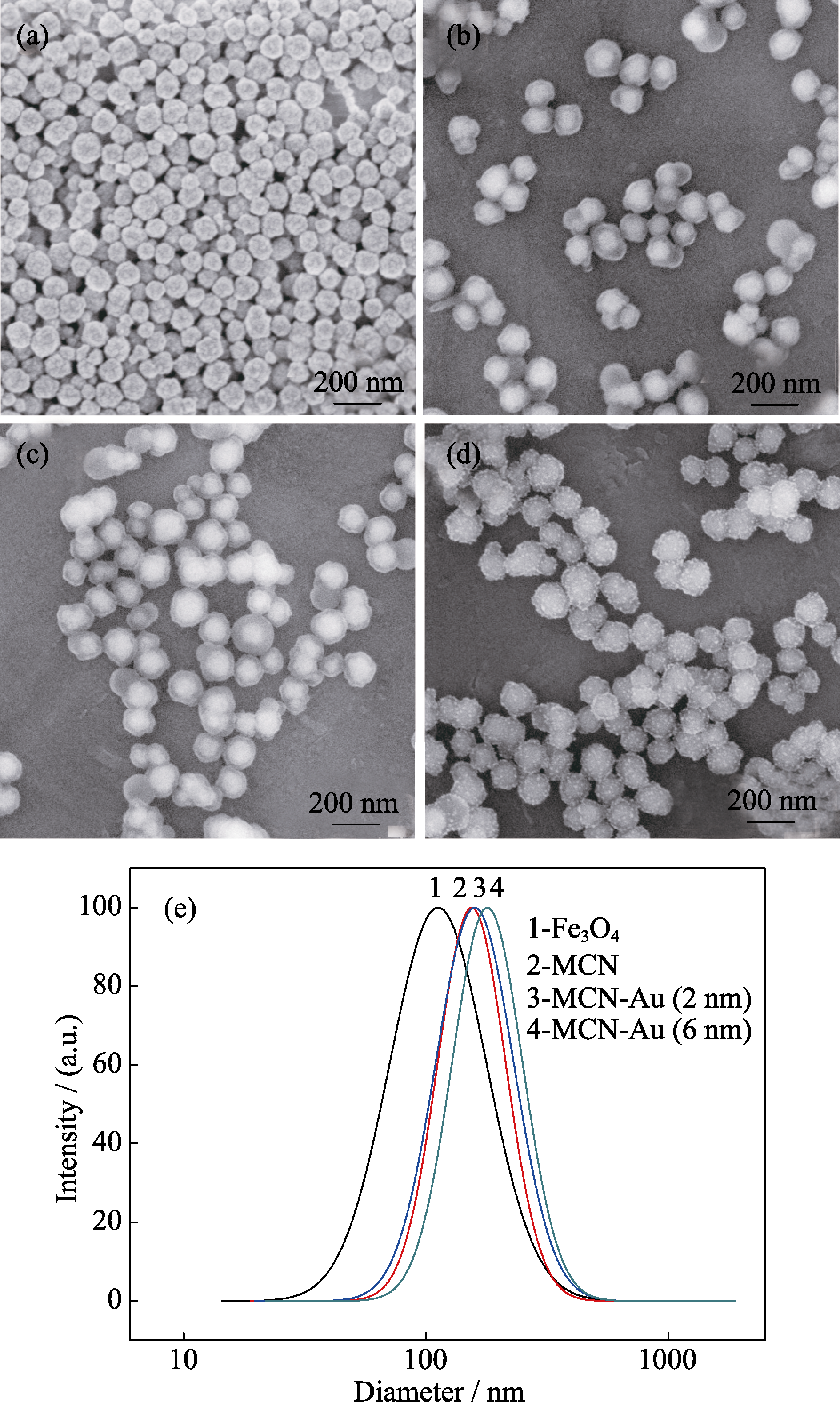
图4 (a) Fe3O4, (b) MCN, (c) MCN-Au (2 nm), (d) MCN-Au (6 nm)的扫描电镜照片; 不同粒子在水相中的动态光散射(DLS)粒径分布曲线
Fig. 4 SEM images of (a) Fe3O4 nanoparticles, (b) MCN, (c) MCN-Au (2 nm), (d) MCN-Au (6 nm); (e) Diameter distribution curves of different particles
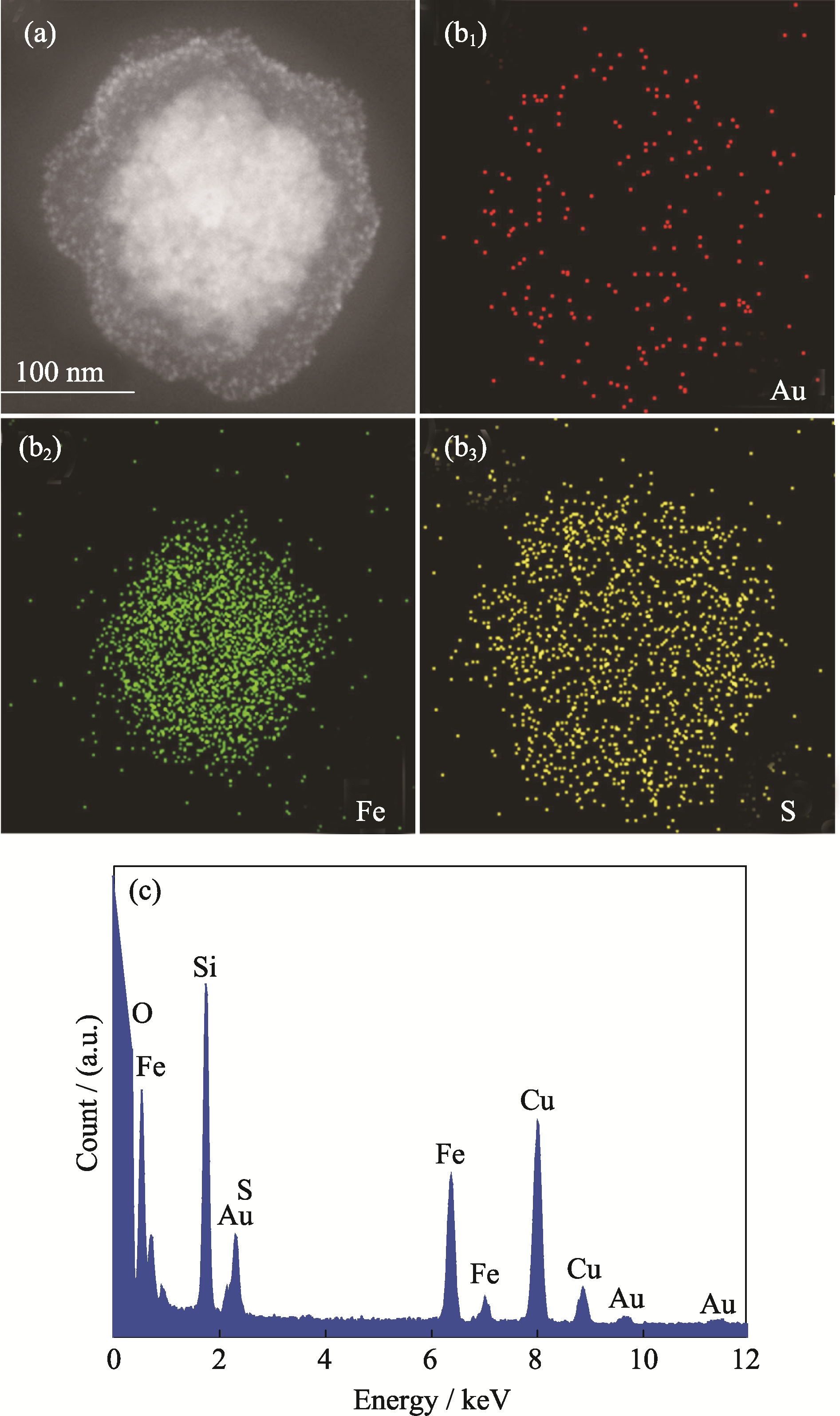
图5 (a) MCN-Au (2 nm)的STEM照片; (b1)金元素、(b2)铁元素和(b3)硫元素的EDS元素面扫描图谱; (c) MCN-Au (2 nm)的能谱图
Fig. 5 STEM image of MCN-Au (2 nm) nanocomposites (a); scanning mapping of Au elements (b1), Fe elements (b2) and S elements (b3). Scale bar is 100 nm; (c) EDS pattern of MCN- Au (2 nm)
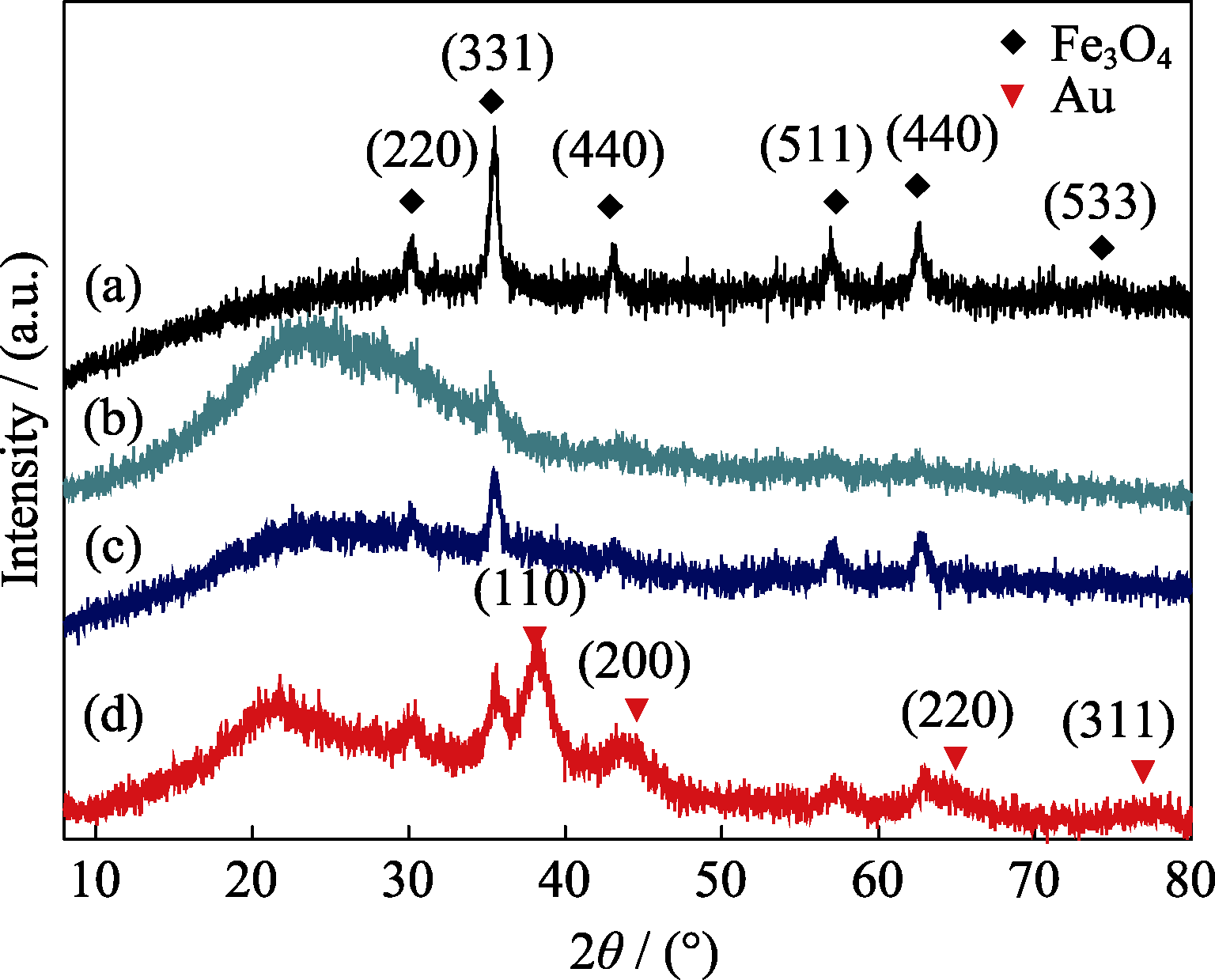
图6 (a) Fe3O4, (b) MCN, (c) MCN-Au (2 nm)和(d) MCN-Au (6 nm)的XRD图谱
Fig. 6 Wide-angle XRD patterns of (a) Fe3O4 nanoparticles, (b) MCN, (c) MCN-Au (2 nm) and (d) MCN-Au (6 nm)
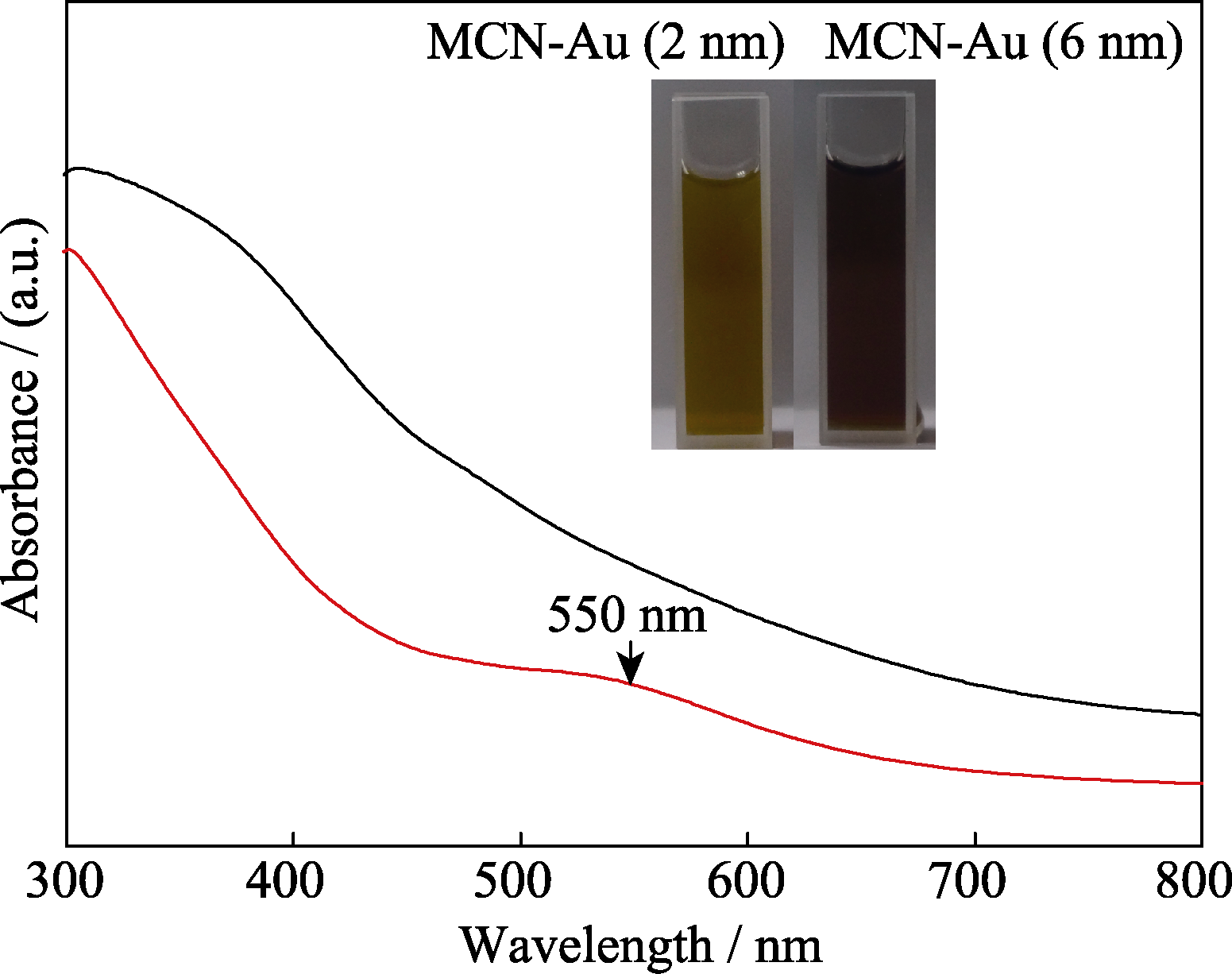
图7 MCN-Au (2 nm) (黑色曲线)和MCN-Au (6 nm) (红色曲线)在水溶液中的紫外吸收光谱谱图
Fig. 7 UV-Vis spectra of (a) MCN-Au (2 nm) (black curve) and (b) MCN-Au (6 nm) (red curve) The insets are the digital photos of MCN-Au (2 nm) and MCN-Au (6 nm)
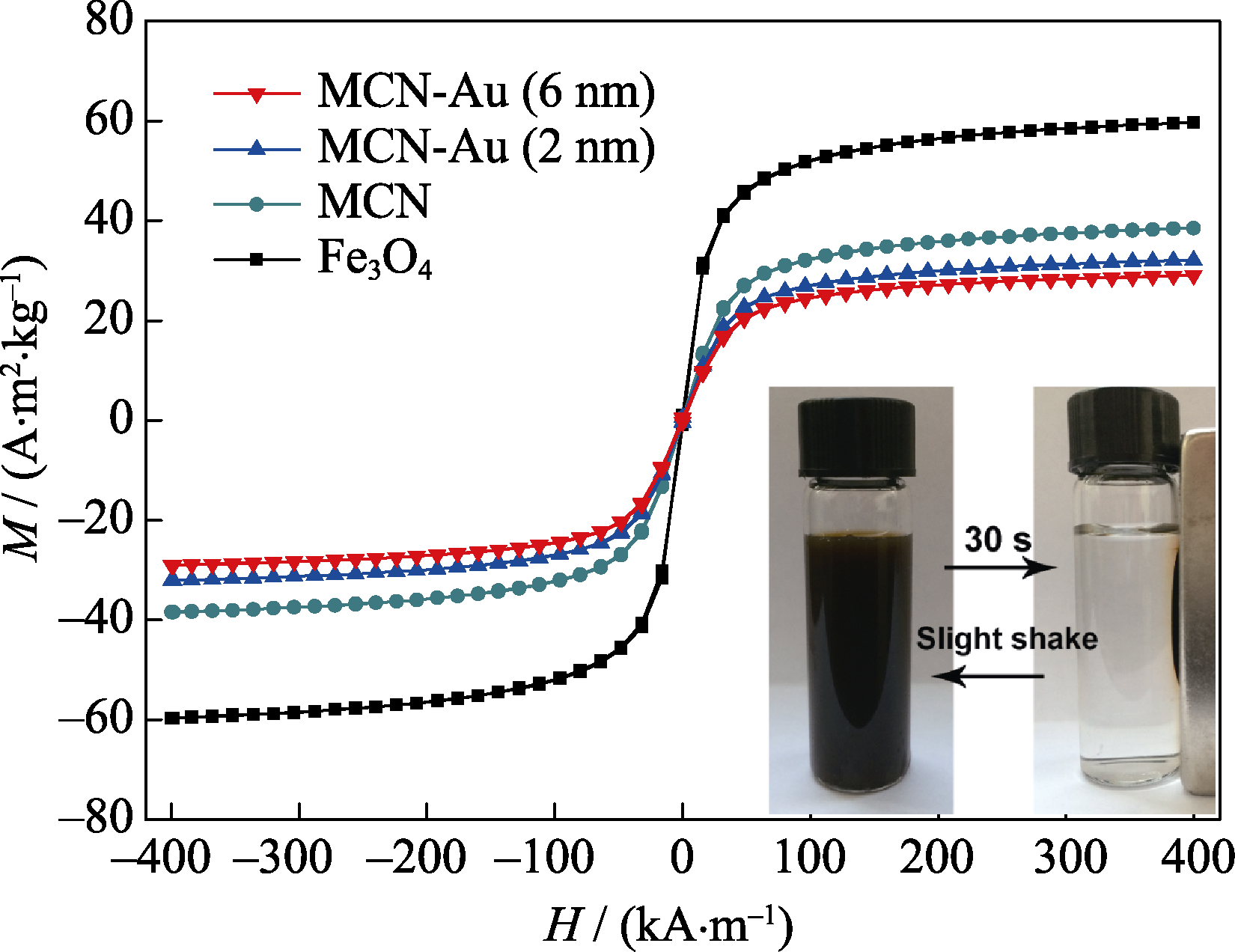
图8 Fe3O4纳米粒子, MCN, MCN-Au (2 nm)和MCN-Au (6 nm)的室温磁滞洄线
Fig. 8 Room-temperature magnetization hysteresis loops of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles, MCN, MCN-Au (2 nm), and MCN-Au (6 nm) The inset is a photograph of the MCN-Au (2 nm) under an external magnetic field
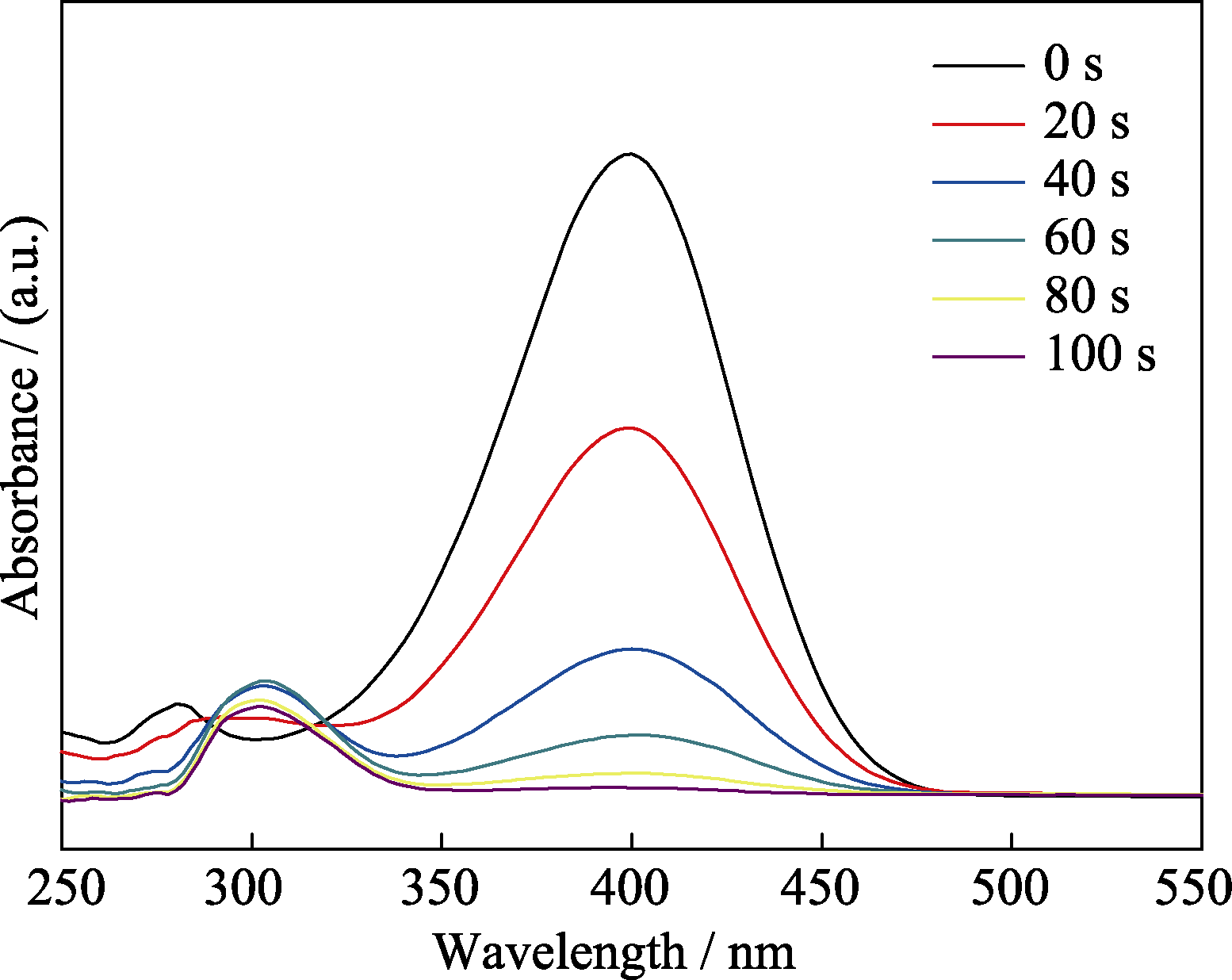
图9 MCN-Au(2 nm)催化4-NP的UV-Vis谱图(每隔20 s测试一次)
Fig. 9 UV-Vis spectra of the reduction of 4-NP in aqueous solution recorded every 20 s using MCN-Au (2 nm) as a catalyst
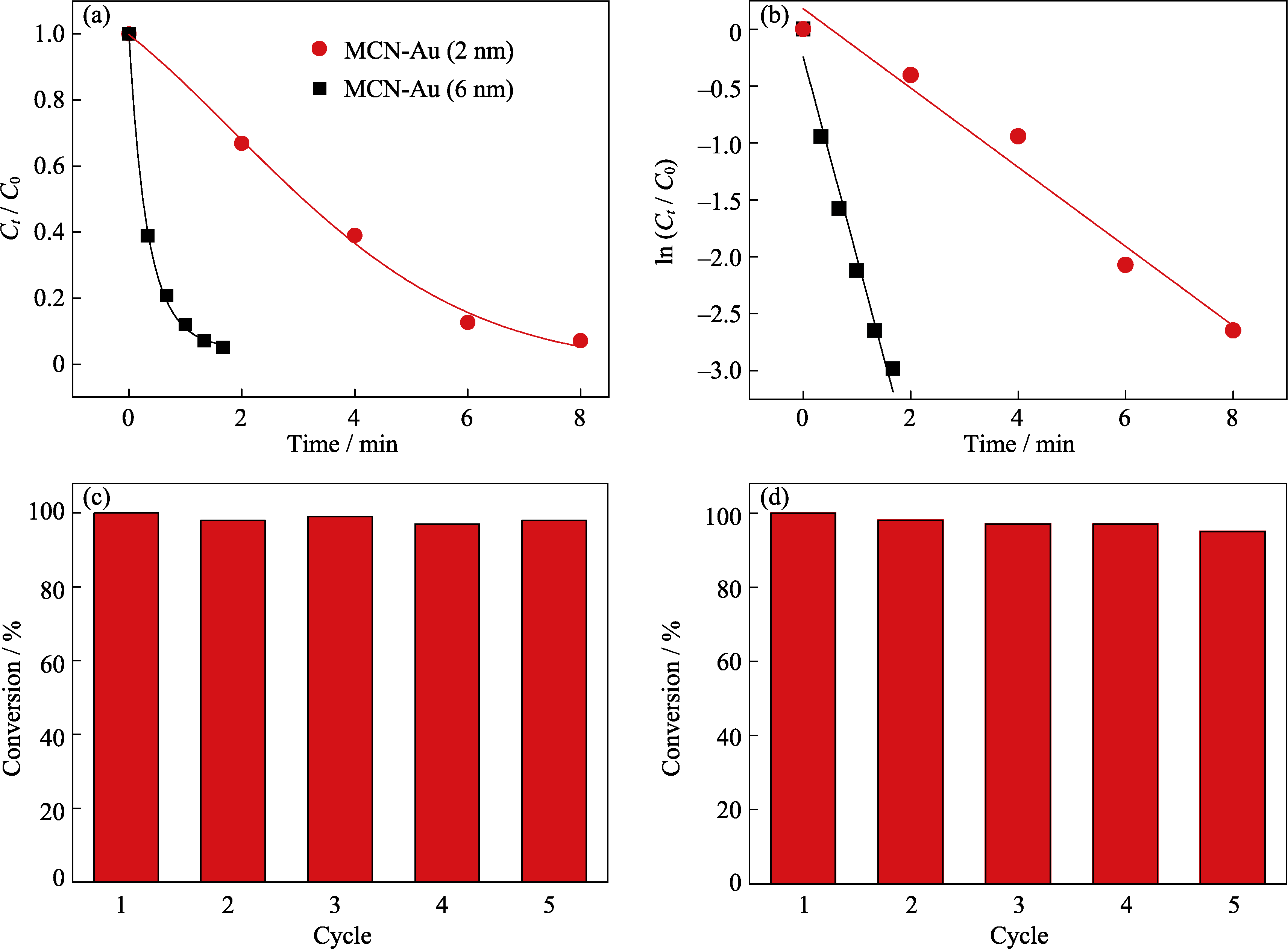
图10 在4-NP催化还原实验中MCN-Au的(a)Ct/C0和(b)ln(Ct/C0)与反应时间的曲线关系; (c)MCN-Au (2 nm)和(d)MCN-Au (6 nm)的循环使用性能测试
Fig. 10 Curves of (a) Ct/C0 and (b) ln(Ct/C0) versus the reaction time for the reduction of 4-NP over MCN-Au; the reusability of the (c) MCN-Au (2 nm) and (d) MCN-Au (6 nm)
| [1] | MA G, BINDER A, CHI M, et al.Stabilizing gold clusters by heterostructured transition-metal oxide-mesoporous silica supports for enhanced catalytic activities for CO oxidation.Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(93): 11413-11415. |
| [2] | BARAKAT T, ROOKE J C, GENTY E, et al.Gold catalysts in environmental remediation and water-gas shift technologies.Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(2): 371-391. |
| [3] | OLIVEIRA R L, KIYOHARAB P K, ROSSI L M.High performance magnetic separation of gold nanoparticles for catalytic oxidation of alcohols.Green Chemistry, 2010, 12(1): 144-149. |
| [4] | LIN F H, DOONG R A.Bifunctional Au-Fe3O4 heterostructures for magnetically recyclable catalysis of nitrophenol reduction.The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(14): 6591-6598. |
| [5] | CUI Y L, CHEN H F, TANG D P, et al.Au(III)-promoted polyaniline gold nanospheres with electrocatalytic recycling of self-produced reactants for signal amplification.Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(83): 10307-10309. |
| [6] | NDOKOYE P, LI X Y, ZHAO Q D, et al.Gold nanostars: benzyldimethylammonium chloride-assisted synthesis, plasmon tuning, SERS and catalytic activity.Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2016, 462: 341-350. |
| [7] | GATES B C.Supported gold catalysts: new properties offered by nanometer and sub-nanometer structures.Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(72): 7876-7877. |
| [8] | TAKALE B S, BAO M, YAMAMOTO Y.Gold nanoparticle (AuNPs) and gold nanopore (AuNPore) catalysts in organic synthesis.Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2014, 12(13): 2005-2027. |
| [9] | KULKARNI A, LOBO-LAPIDUS R J, GATES B C. Metal clusters on supports: synthesis, structure, reactivity, and catalytic properties.Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(33): 5997-6015. |
| [10] | LIU G Y, JI H F, YANG X L, et al.Synthesis of a Au/silica/polymer trilayer composite and the corresponding hollow polymer microsphere with a movable Au core.Langmuir, 2008, 24(3): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | YUAN C H, LUO W A, ZHONG L N, et al.Gold@polymer nanostructures with tunable permeability shells for selective catalysis.Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(15): 3515-3519. |
| [12] | LIU Y C, LI M L, CHEN G F.A new type of raspberry-like polymer composite submicrospheres with tunable gold nanoparticles coverage and their enhanced catalytic properties.Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(3): 930-937. |
| [13] | SONG W, FERRANDEZ D M P, HAANDEL L V, et al. Selective propylene oxidation to acrolein by gold dispersed on MgCuCr2O4 spinel.ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(2): 1100-1111. |
| [14] | LI Z X, XUE W, GUAN B T, et al.A conceptual translation of homogeneous catalysis into heterogeneous catalysis: homogeneous-like heterogeneous gold nanoparticle catalyst induced by ceria supporter.Nanoscale, 2013, 5(3): 1213-1220. |
| [15] | BEHL M, JAIN P K.Catalytic activation of a solid oxide in electronic contact with gold nanoparticles.Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(3): 992-997. |
| [16] | ZHU C Z, HAN L, HU P, et al.Loading of well-dispersed gold nanoparticles on two-dimensional graphene oxide/SiO2 composite nanosheets and their catalytic properties.Nanoscale, 2012, 4(5): 1641-1646. |
| [17] | LI J, LIU C Y, LIU Y.Au/graphene hydrogel: synthesis, characterization and its use for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol.Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(17): 8426-8430. |
| [18] | ZHANG Z Y, SHAO C L, ZOU P, et al.In situ assembly of well-dispersed gold nanoparticles on electrospun silica nanotubes for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol.Chemical Communications, 2011, 47(13): 3906-3908. |
| [19] | WANG D W, ZHU X M, LEE S F, et al.Folate-conjugated Fe3O4@SiO2@gold nanorods@mesoporous SiO2 hybrid nanomaterial: a theranostic agent for magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal therapy.Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013, 1(23): 2934-2942. |
| [20] | WANG Z H, FU H F, HAN D M, et al.The effects of Au species and surfactant on the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol by Au@SiO2.Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(47): 20374-20381. |
| [21] | MUNNIK P, DE JONGH P E, DE JONG K P. Recent developments in the synthesis of supported catalysts.Chemical Reviews, 2015, 115(14): 6687-6718. |
| [22] | GAWANDE M B, GOSWAMI A, ASEFA T, et al.Core-shell nanoparticles: synthesis and applications in catalysis and electrocatalysis.Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(21): 7540-7590. |
| [23] | SHYLESH S, SCHÜNEMANN V, THIEL W R. Magnetically separable nanocatalysts: bridges between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis.Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(20): 3428-3459. |
| [24] | LIU J, QIAO S Z, HU Q H, et al.Magnetic nanocomposites with mesoporous structures: synthesis and applications.Small, 2011, 7(4): 425-443. |
| [25] | WANG D, ASTRUC D.Fast-growing field of magnetically recyclable nanocatalysts.Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(14): 6949-6985. |
| [26] | WANG L Y, LUO J, FAN Q, et al.Monodispersed core-shell Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles.Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005, 109(46): 21593. |
| [27] | RAHMAN Z U, DONG Y L, SU L, et al.Mesostructured multifunctional magnetic nanocomposites for potential applications.Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 222(15): 382-390. |
| [28] | ZHU Y H, SHEN J H, ZHOU K F, et al.Multifunctional magnetic composite microspheres with in situ growth Au nanoparticles: a highly efficient catalyst system.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(5): 1614-1619. |
| [29] | LIN F H, DOONG R A.Highly efficient reduction of 4-nitrophenol by heterostructured gold-magnetite nanocatalysts.Applied Catalysis A General, 2014, 486: 32-41. |
| [30] | YAO T J, CUI T Y, WANG H, et al.A simple way to prepare Au@polypyrrole/Fe3O4 hollow capsules with high stability and their application in catalytic reduction of methylene blue dye.Nanoscale, 2014, 6(13): 7666-7674. |
| [31] | XUAN S H, WANG Y X, YU J C, et al.Preparation, characterization, and catalytic activity of core/shell Fe3O4@polyaniline@Au nanocomposites.Langmuir, 2009, 25(19): 11835-11843. |
| [32] | WANG C, CHEN J, ZHOU X, et al.Magnetic yolk-shell mesoporous silica microspheres with supported Au nanoparticles as recyclable high-performance nanocatalysts.Nano Research, 2015, 8(1): 238-245. |
| [33] | ZENG T, ZHANG X L, WANG S H, et al.A double-shelled yolk-like structure as an ideal magnetic support of tiny gold nanoparticles for nitrophenol reduction.Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(38): 11641-11647. |
| [34] | ZHENG J M, DONG Y L, WANG W F, et al.In situ loading of gold nanoparticles on Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic nanocomposites and their high catalytic activity.Nanoscale, 2013, 5(11): 4894-4901. |
| [35] | ZHU X Y, GU J L, LI Y S, et al.Magnetic core-mesoporous shell nanocarriers with drug anchorages suspended in mesopore interior for cisplatin delivery.Microporous & Mesoporous Materials, 2014, 196: 115-121. |
| [36] | DONG W J, LI Y S, NIU D C, et al.Facile synthesis of monodisperse superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Core@hybrid@Au shell nanocomposite for bimodal imaging and photothermal therapy.Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(45): 5392-5397. |
| [37] | DONG W J, LI Y S, NIU D C, et al.A simple route to prepare monodisperse Au NP-decorated, dye-doped, superparamagnetic nanocomposites for optical, MR, and CT trimodal imaging.Small, 2013, 9(15): 2500-2508. |
| [38] | GAO Y P, GU J L, LI L, et al.Synthesis of gold nanoshells through improved seed-mediated growth approach: brust-like, in situ seed formation.Langmuir, 2016, 32(9): 2251-2258. |
| [39] | ZHAI Y G, DONG W J, GAO Y P, et al.Preparation of superparamagnetic gold nanocomposites with different diameters and their imaging and therapy applications.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(9): 951-955. |
| [40] | LIU G Q, WANG D A, ZHOU F, et al.Electrostatic self-assembly of Au nanoparticles onto thermosensitive magnetic core-shell microgels for thermally tunable and magnetically recyclable catalysis.Small, 2015, 11(23): 2807-2816. |
| [41] | GU S S, WUNDER S, LU Y, et al.Kinetic analysis of the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol by metallic nanoparticles.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(32): 18618-18625. |
| [42] | WUNDER S, LU Y, ALBRECHT M, et al.Catalytic activity of faceted gold nanoparticles studied by a model reaction: evidence for substrate-induced surface restructuring.ACS Catalysis, 2011, 1(8): 908-916. |
| [43] | HVOLBÆK B, JANSSENS T V W, CLAUSEN B S, et al. Catalytic activity of Au nanoparticles.Nano Today, 2007, 2(4): 14-18. |
| [44] | SHIVHARE A, AMBROSE S J, ZHANG H, et al.Stable and recyclable Au25 clusters for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol.Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(3): 276-278. |
| [45] | CAO J, MEI S L, JIA H, et al.In situ synthesis of catalytic active Au nanoparticles onto gibbsite-polydopamine core-shell nanoplates.Langmuir, 2015, 31(34): 9483-9491. |
| [46] | WOO H, KANG H P.Hybrid Au nanoparticles on Fe3O4 @polymer as efficient catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol.Catalysis Communications, 2014, 46(5): 133-137. |
| [47] | LIN F H, DOONG R A.Catalytic nanoreactors of Au@Fe3O4 yolk-shell nanostructures with various Au sizes for efficient nitroarenes reduction.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(14): 7844-7853. |
| [48] | WANG Y, LI H, ZHANG J J, et al.Fe3O4 and Au nanoparticles dispersed on the graphene support as a highly active catalyst toward the reduction of 4-nitrophenol.Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18(1): 615-623. |
| [1] | 付宇坤, 曾敏, 饶先发, 钟盛文, 张慧娟, 姚文俐. 锂离子电池高镍LiNi0.8Mn0.2O2正极材料的微波合成及其Co、Al共改性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 718-724. |
| [2] | 文子聪, 牛德超, 李永生. 负载银簇的硅基杂化纳米颗粒制备及其SERS性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1297-1304. |
| [3] | 王琦, 彭大春, 马倩, 何月德, 刘洪波. 炭包覆LiFePO4纳米片的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(12): 1349-1354. |
| [4] | 孟方礼, 章冬云, 常程康, 徐家跃, KAMZIN A S. 基于铁粉还原的LiFePO4/C合成路径及其电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(8): 802-806. |
| [5] | 马国强, 温兆银, 王清松, 靳 俊, 吴相伟, 张敬超. CeO2纳米晶的添加对锂硫电池电化学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(9): 913-918. |
| [6] | 王 军, 张宝林, 杨 高, 王 磊, 谢松伯, 李 璇, 郜发宝. 磁性氧化铁高效磁共振造影剂的制备及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(1): 53-58. |
| [7] | 陈飞彪, 王英男, 吴伯荣, 熊云奎, 廖维林, 吴 锋, 孙 喆. 锂硫电池石墨烯/硫复合正极材料的制备及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(6): 627-632. |
| [8] | 刘 玲, 袁中直, 邱彩霞, 程思洁, 刘金成. 新型锂离子电池材料FeS2/VGCF的合成与电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(12): 1291-1295. |
| [9] | 陈 龙, 刘景东, 张诗群. 负载ZnS的介孔炭复合硫正极材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(10): 1127-1131. |
| [10] | 曾晓波, 胡 灏, 解丽芹, 蓝 芳, 吴 尧, 顾忠伟. 超顺磁性磷酸钙复合支架的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(1): 79-84. |
| [11] | 刘双科, 许 静, 李德湛, 胡 芸, 谢 凯. 间苯二酚–甲醛辅助溶胶–凝胶法制备纳米Li2MnSiO4/C正极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(06): 635-638. |
| [12] | 华 宁, 王辰云, 康雪雅, 吐尔迪, 韩 英. 碳热还原法制备Zn掺杂的LiFePO4及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(8): 887-892. |
| [13] | 江 雯,温贤涛,王 伟,吴 尧,顾忠伟. 超顺磁单分散性Fe3O4磁纳米粒的制备及性能表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(4): 727-731. |
| [14] | 马文哲,钱雪峰,印杰,朱子康. 空心超顺磁性Fe3O4纳米微球的制备与表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(6): 1407-1410. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||