无机材料学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 162-172.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170346 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20170346
董丽颖, 张永刚, 朱英杰
收稿日期:2017-07-20
修回日期:2017-10-25
出版日期:2018-02-26
网络出版日期:2018-01-26
作者简介:董丽颖(1985),女,博士.E-mail:lydong@mail.sic.ac.cn
基金资助:DONG Li-Ying, ZHANG Yong-Gang, ZHU Ying-Jie
Received:2017-07-20
Revised:2017-10-25
Published:2018-02-26
Online:2018-01-26
Supported by:摘要:
新型无机耐火纸是以羟基磷灰石超长纳米线作为原料制备而成的, 具有优良的生物相容性、环境友好、物理强度性能好、柔韧性高、耐高温、不燃烧、可用于书写和彩色打印, 有望用于档案等重要文件的长久保存。目前, 已制备出具有多种功能和用途的羟基磷灰石超长纳米线基新型纸张, 包括抗菌耐火纸、防水耐火纸、荧光耐火纸、耐高温标签纸、光(电)缆用阻燃耐火包带、快速检测试纸、生物医用纸、高效过滤纸等。新型无机耐火纸在特种纸、吸附过滤、生物医学、隔热、耐高温、环境保护、能源等领域展现出广阔的应用前景。本文综述了最近几年来新型羟基磷灰石超长纳米线基耐火纸研究取得的一些重要进展, 并且对该新型无机耐火纸未来的应用和产业化进行了展望。
中图分类号:
董丽颖, 张永刚, 朱英杰. 新型无机耐火纸[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(2): 162-172.
DONG Li-Ying, ZHANG Yong-Gang, ZHU Ying-Jie. A New Kind of Fire-resistant Inorganic Paper[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(2): 162-172.
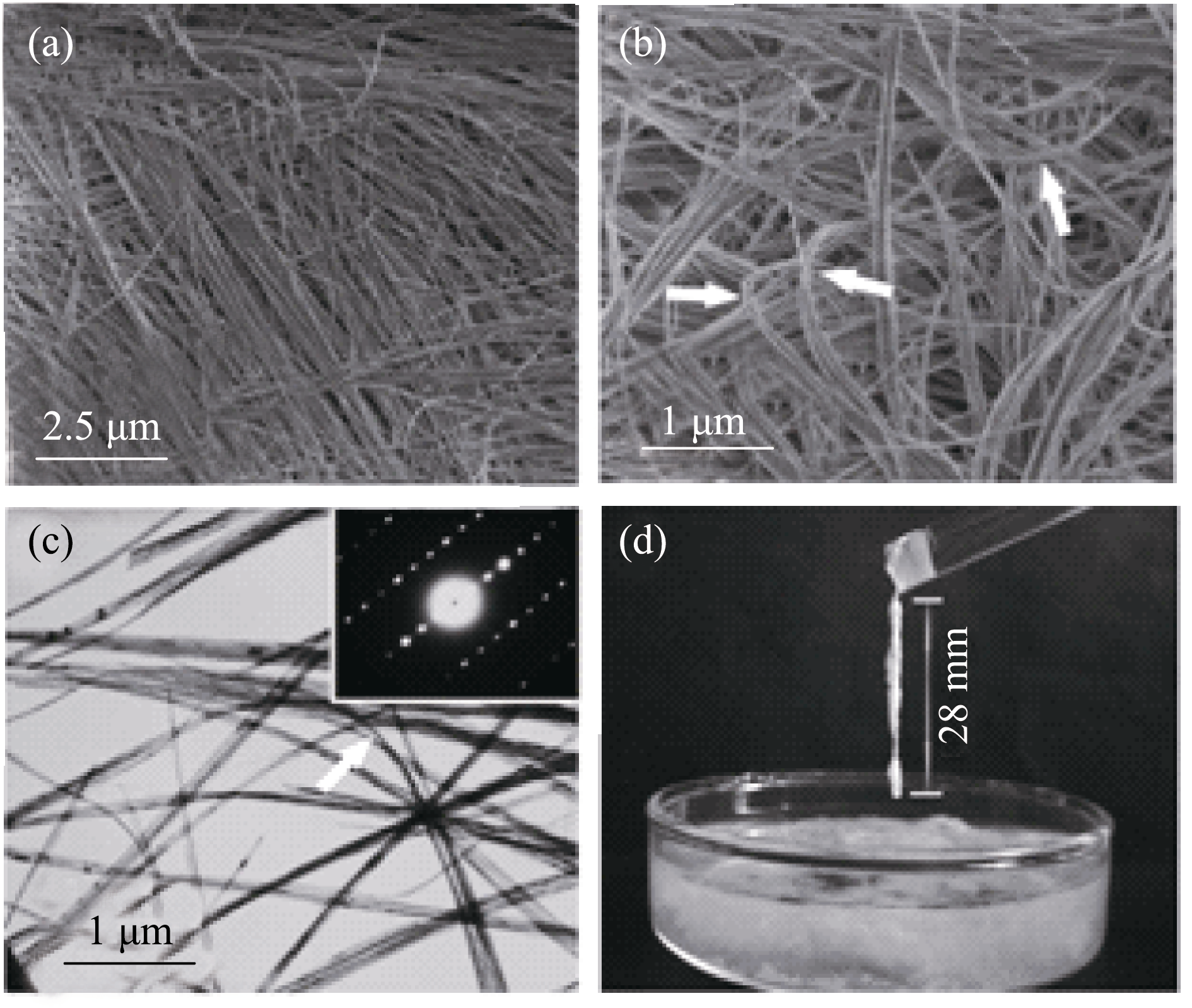
图1 采用溶剂热法以油酸钙作为前驱体合成的高柔韧性HAP超长纳米线[12]
Fig. 1 Highly flexible ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires prepared by the calcium oleate precursor solvothermal method[12] (a, b) SEM micrographs; (c) TEM micrograph with inset showing a SAED (selected-area electron diffraction) pattern of a single ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowire; (d) The formation of a long fiber with a length of ~28 mm from an ethanol dispersion of ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires

图2 (a) 新型HAP超长纳米线耐火纸的数码照片和(b) 用喷墨打印机在HAP超长纳米线耐火纸上打印的不同颜色图案和文字的数码照片[12]
Fig. 2 (a) A digital image of the new kind of highly flexible fire-resistant paper made from ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires; (b) English words and Chinese characters with different colors printed on the fire-resistant ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowire paper by using a commercial ink-jet printer[12]

图3 制备的A4尺寸(21 cm×29.7 cm)的HAP超长纳米线耐火纸的数码照片[29]
Fig. 3 Digital images of the highly flexible fire-resistant ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowire paper with an A4 size[29]

图4 新型高柔韧性HAP超长纳米线耐火纸的耐火性能、热稳定性及其与普通复印纸的对比实验[12]
Fig. 4 Illustration of the excellent fire-resistance and high- temperature resistance of the as-prepared highly flexible fire- resistant paper based on ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires, and the commercial cellulose paper is used for comparison[12]
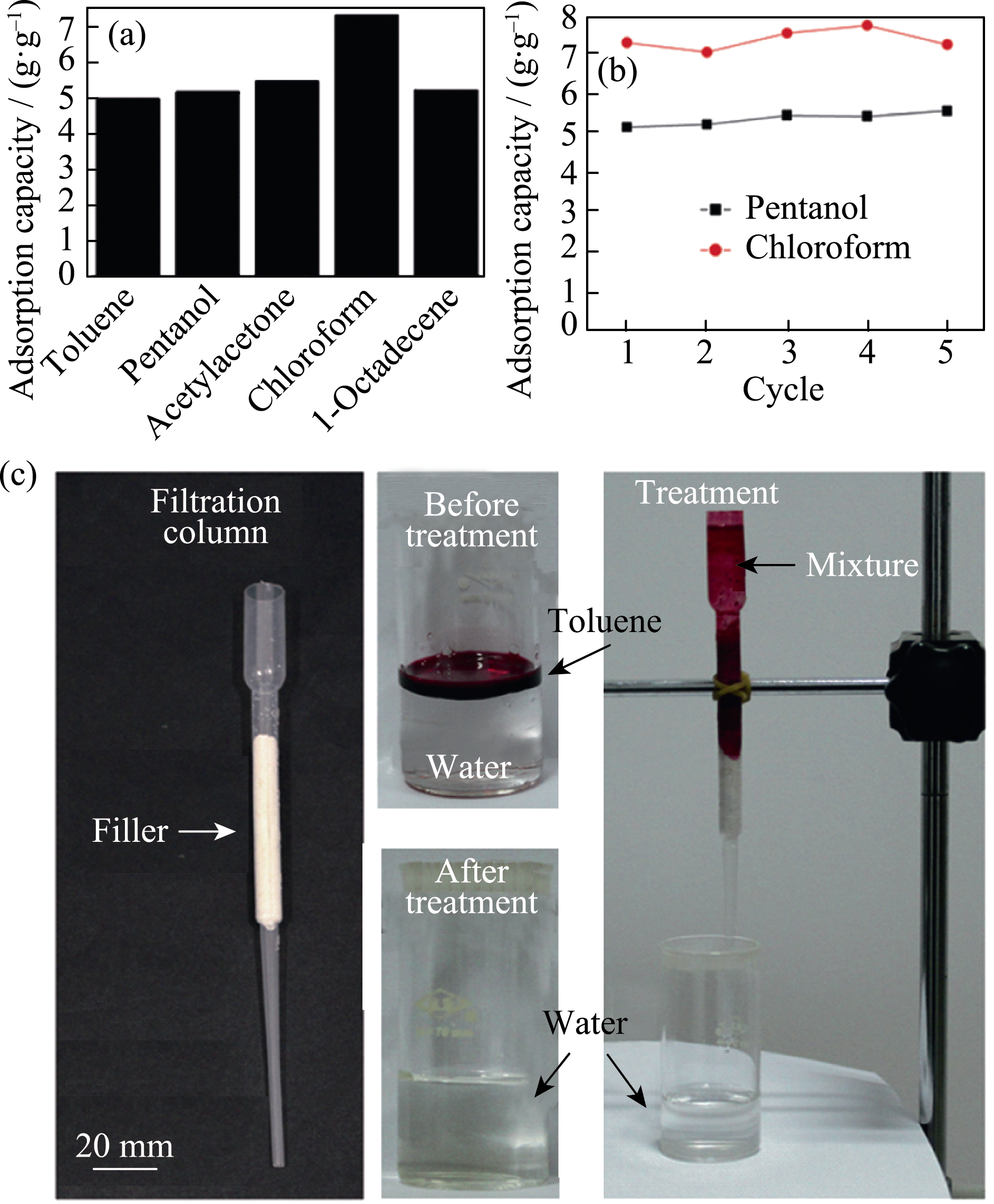
图5 HAP超长纳米线耐火纸对有机污染物的吸附性能[12]
Fig. 5 Adsorption properties of the highly flexible fire-resistant paper made from ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires[12]
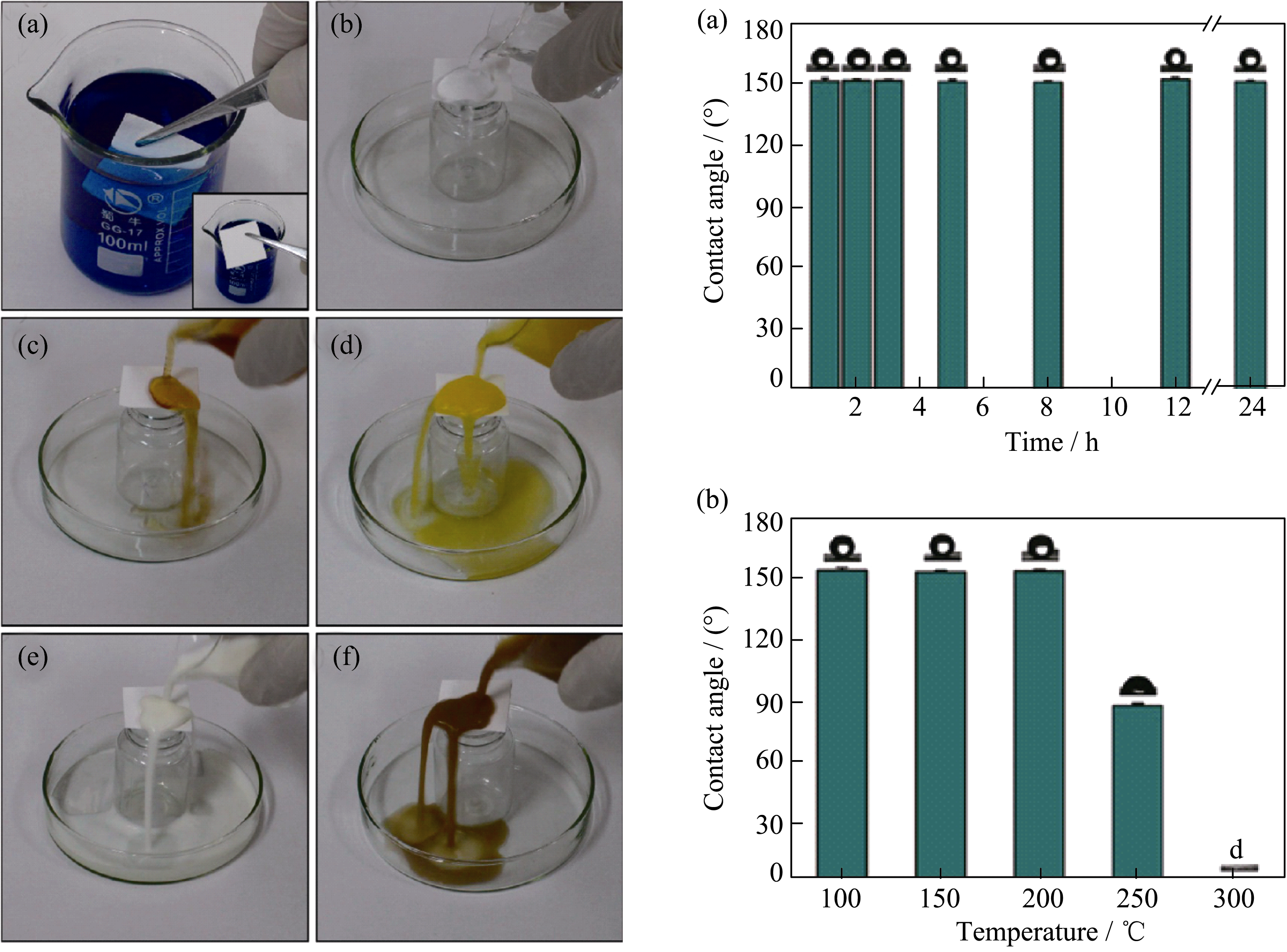
图6 新型HAP超长纳米线防水耐火纸对水和多种商业饮料具有优良的超疏水性能和优异的热稳定性[38]
Fig. 6 Liquid repellency tests for a new kind of fire-resistant superhydrophobic layered paper based on ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires and its excellent thermal stability[38]

图8 制备的90wt% HAP超长纳米线/壳聚糖复合生物纸的数码照片和力学性能[44]
Fig. 8 Digital images and the shear stress-strain curves of the as-prepared 90wt% ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowire/chitosan biopaper[44]

图9 普通植物纤维纸(a)和Tb3+掺杂HAP超长纳米线荧光耐火纸(b)在热处理前后的数码照片; (c) 制备的Tb3+掺杂HAP超长纳米线荧光耐火纸300℃处理60 min后在紫外光(~365 nm)照射下发光性能保持良好; (d) 制备的Tb3+掺杂HAP超长纳米线荧光耐火纸和普通植物纤维纸在热处理前后的白度变化[51]
Fig. 9 Digital images of two kind of paper sheets before and after thermal treatment

图10 研制的新型羟基磷灰石超长纳米线基过滤纸在各种不同程度的污染环境中对空气PM2.5细颗粒物的过滤效率均高于95%, 而且可以多次重复和长时间使用[54]
Fig. 10 PM2.5 removal efficiencies of the as-prepared new kind of HAP nanowire-based filtration paper[54]
| [1] | 法国国家图书馆遭遇水灾一万余部书籍被淹[EB/OL]. [2017- 10-25]. . |
| [2] | 俄图书馆失火百万史料焚毁[EB/OL]. [2017-10-25]. . |
| [3] | CHEN F, ZHU Y J.Multifunctional calcium phosphate nanostructured materials and biomedical applications.Current Nanoscience, 2014, 10(4): 465-485. |
| [4] | HUI J F, WANG X.Hydroxyapatite nanocrystals: colloidal chemistry, assembly and their biological applications.Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2014, 1(3): 215-225. |
| [5] | ŠUPOVÁ M.Substituted hydroxyapatites for biomedical applications: a review.Ceramics International, 2015, 41(8): 9203-9231. |
| [6] | HAIDER A, HAIDER S, HAN S S, et al.Recent advances in the synthesis, functionalization and biomedical applications of hydroxyapatite: a review.RSC Advances, 2017, 7(13): 7442-7458. |
| [7] | CHEN F, HUANG P, ZHU Y J, et al.The photoluminescence, drug delivery and imaging properties of multifunctional Eu3+/Gd3+ dual-doped hydroxyapatite nanorods.Biomaterials, 2011, 32(34): 9031-9039. |
| [8] | LIU C S, HUANG Y, CUI J H.Kinetics of hydroxyapatite precipitation at pH 10 to 11.Biomaterials, 2001, 22(4): 301-306. |
| [9] | ZHANG C M, LI C X, HUANG S S, et al.Self-activated luminescent and mesoporous strontium hydroxyapatite nanorods for drug delivery. Biomaterials, 2010, 31(12): 3374-3383. |
| [10] | ZHU Y J, CHEN F.Microwave-assisted synthesis of calcium phosphate nanostructured materials in liquid phase.Progress in Chemistry, 2015, 27(5): 459-471. |
| [11] | CHENG Y, WANG M, WANG X X, et al.Investigation on in vitro osteogenic properties of multiple-doped hydroxyapatite with natural bone content.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(12): 1341-1346. |
| [12] | LU B Q, ZHU Y J, CHEN F.Highly flexible and noninflammable inorganic hydroxyapatite paper.Chemistry-A European Journal, 2014, 20(5): 1242-1246. |
| [13] | KANDORI K, KURODA T, TOGASHI S, et al.Preparation of calcium hydroxyapatite nanoparticles using microreactor and their characteristics of protein adsorption.Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2011, 115(4): 653-659. |
| [14] | ANWAR A, REHMAN I U, DARR J A.Low-temperature synthesis and surface modification of high surface area calcium hydroxyapatite nanorods incorporating organofunctionalized surfaces.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(51): 29069-29076. |
| [15] | CHEN H F, SUN K, TANG Z Y, et al.Synthesis of fluorapatite nanorods and nanowires by direct precipitation from solution.Crystal Growth & Design, 2006, 6(6): 1504-1508. |
| [16] | LV B Y, ZHAO L S, PU Y, et al.Facile preparation of controllable- aspect-ratio hydroxyapatite nanorods with high-gravity technology for bone tissue engineering. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(11): 2976-2983. |
| [17] | ZHAO X Y, ZHU Y J, LU B Q, et al.Hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanorods using pyridoxal-5°-phosphate as a phosphorus source.Materials Research Bulletin, 2014, 55: 67-70. |
| [18] | MA M G, ZHU Y J, CHANG J.Monetite formed in mixed solvents of water and ethylene glycol and its transformation to hydroxyapatite.Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(29): 14226-14230. |
| [19] | ZHAO X Y, ZHU Y J, QI C, et al.Hierarchical hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres: microwave-assisted rapid synthesis by using pyridoxal-5’-phosphate as a phosphorus source and application in drug delivery.Chemistry-An Asian Journal, 2013, 8(6): 1313-1320. |
| [20] | ZHAO J, ZHU Y J, CHENG G F, et al.Microwave-assisted hydrothermal rapid synthesis of amorphous calcium phosphate nanoparticles and hydroxyapatite microspheres using cytidine 5’-triphosphate disodium salt as a phosphate source.Materials Letters, 2014, 124: 208-211. |
| [21] | PARK S Y, KIM K I, PARK S P, et al.Aspartic acid-assisted synthesis of multifunctional strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite microspheres.Crystal Growth & Design, 2016, 16(8): 4318-4326. |
| [22] | CHEN F, ZHU Y J, WANG K W, et al.Surfactant-free solvothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanowire/nanotube ordered arrays with biomimetic structures.CrystEngComm, 2011, 13(6): 1858-1863. |
| [23] | ZHAO X Y, ZHU Y J, CHEN F, et al.Hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanorods and nanowires using riboflavin-5’- phosphate monosodium salt as a new phosphorus source and their application in protein adsorption.CrystEngComm, 2013, 15(39): 7926-7935. |
| [24] | BRAMHE S, KIM T N, BALAKRISHNAN A, et al.Conversion from biowaste venerupis clam shells to hydroxyapatite nanowires.Materials Letters, 2014, 135: 195-198. |
| [25] | AI M, DU Z Y, ZHU S Q, et al.Composite resin reinforced with silver nanoparticles-laden hydroxyapatite nanowires for dental application.Dental Materials, 2017, 33(1): 12-22. |
| [26] | HE J Y, ZHANG K S, WU S B, et al.Performance of novel hydroxyapatite nanowires in treatment of fluoride contaminated water.Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 303(13): 119-130. |
| [27] | JIANG Y Y, ZHU Y J, CHEN F, et al.Solvothermal synthesis of submillimeter ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires using a calcium oleate precursor in a series of monohydroxy alcohols.Ceramics International, 2015, 41(4): 6098-6102. |
| [28] | ZHANG Y G, ZHU Y J, CHEN F, et al.Ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires synthesized by solvothermal treatment using a series of phosphate sodium salts.Materials Letters, 2015, 144: 135-137. |
| [29] | LI H, ZHU Y J, JIANG Y Y, et al.Hierarchical assembly of monodisperse hydroxyapatite nanowires and construction of high-strength fire-resistant inorganic paper with high-temperature flexibility.ChemNanoMat, 2017, 3(4): 259-268. |
| [30] | QI C, TANG Q L, ZHU Y J, et al.Microwave-assisted hydrothermal rapid synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanowires using adenosine 5'-triphosphate disodium salt as phosphorus source.Materials Letters, 2012, 85: 71-73. |
| [31] | LIN K L, LIU X G, CHANG J, et al.Facile synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles, nanowires and hollow nano-structured microspheres using similar structured hard-precursors.Nanoscale, 2011, 3(8): 3052-3055. |
| [32] | YANG Z, HUANG Y, CHEN S T, et al.Template synthesis of highly ordered hydroxyapatite nanowire arrays.Journal of Materials Science, 2005, 40(5): 1121-1125. |
| [33] | COSTA D O, DIXON S J, RIZKALLA A S.One- and three-dimensional growth of hydroxyapatite nanowires during sol-gel-hydrothermal synthesis.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2012, 4(3): 1490-1499. |
| [34] | CAO M H, WANG Y H, GUO C X, et al.Preparation of ultrahigh-aspect-ratio hydroxyapatite nanofibers in reverse micelles under hydrothermal conditions.Langmuir, 2004, 20(11): 4784-4786. |
| [35] | CHEN F, ZHU Y J.Large-scale automated production of highly ordered ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires and construction of various fire-resistant flexible ordered architectures.ACS Nano, 2016, 10(12), 11483-11495. |
| [36] | VORONOV R S, PAPAVASSILIOU D V, LEE L L.Review of fluid slip over superhydrophobic surfaces and its dependence on the contact angle.Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(8): 2455-2477. |
| [37] | DYETT B P, WU A H, LAMB R N.Mechanical stability of surface architecture—consequences for superhydrophobicity.ACS Applied Materilas & Interfaces, 2014, 6(21): 18380-18394. |
| [38] | CHEN F F, ZHU Y J, XIONG Z C, et al.Highly flexible superhydrophobic and fire-resistant layered inorganic paper.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(50): 34715-34724. |
| [39] | CHEN F F, ZHU Y J, XIONG Z C, et al.Inorganic nanowires-assembled layered paper as the valve for controlling water transportation.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(12): 11045-11053. |
| [40] | XIONG Z C, ZHU Y J, CHEN F F, et al.One-step synthesis of silver nanoparticle-decorated hydroxyapatite nanowires for the construction of highly flexible free-standing paper with high antibacterial activity.Chemistry-A European Journal, 2016, 22(32): 11224-11231. |
| [41] | XIONG Z C, YANG Z Y, ZHU Y J, et al.Ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires-based paper co-loaded with silver nanoparticles and antibiotic for long-term antibacterial benefit.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(27): 22212-22222. |
| [42] | DONG L Y, ZHU Y J.A new kind of fireproof, flexible, inorganic, nanocomposite paper and its application to the protection layer in flame-retardant fiber-optic cables.Chemistry-A European Journal, 2017, 23(19): 4597-4604. |
| [43] | CHEN F F, ZHU Y J, XIONG Z C, et al.Hydroxyapatite nanowires@metal-organic framework core/shell nanofibers: templated synthesis, peroxidase-like activity, and derived flexible recyclable test paper.Chemistry-A European Journal, 2017, 23(14): 3328-3337. |
| [44] | SUN T W, ZHU Y J, CHEN F.Highly flexible multifunctional biopaper comprising chitosan reinforced by ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires.Chemistry-A European Journal, 2017, 23(16): 3850-3862. |
| [45] | SUN T W, ZHU Y J, CHEN F, et al.Ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowire/collagen biopaper with high flexibility, improved mechanical properties and excellent cellular attachment.Chemistry-An Asian Journal, 2017, 12(6): 655-664. |
| [46] | XIE Y F, HE W M, LI F, et al.Luminescence enhanced Eu3+/Gd3+ co-doped hydroxyapatite nanocrystals as imaging agents in vitro and in vivo.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(16): 10212-10219. |
| [47] | ZHENG X Y, LIU M Y, HUI J F, et al.Ln3+-doped hydroxyapatite nanocrystals: controllable synthesis and cell imaging.Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17(31): 20301-20307. |
| [48] | PERERA T S H, HAN Y C, LU X F, et al. Rare earth doped apatite nanomaterials for biological application. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2015: 705390. |
| [49] | SUN Y X, YANG H, TAO D L.Preparation and characterization of Eu3+-doped fluorapatite nanoparticles by a hydrothermal method.Ceramics International, 2012, 38(8): 6937-6941. |
| [50] | TESCH A, WENISCH C, HERRMANN K H, et al.Luminomagnetic Eu3+ and Dy3+-doped hydroxyapatite for multimodal imaging.Materials Science & Engineering C, 2017, 81: 422-431. |
| [51] | YANG R L, ZHU Y J, CHEN F F, et al.Luminescent, fire-resistant and water-proof ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires-based paper for multimode anti-counterfeiting application.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(30): 25455-25464. |
| [52] | TAO J, ZHANG L M, CAO J J, et al.A review of current knowledge concerning PM2.5 chemical composition, aerosol optical properties and their relationships across china.Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2017, 17(15): 9485-9518. |
| [53] | BO M, SALIZZONI P, CLERICO M, et al. Assessment of indoor-outdoor particulate matter air pollution: a review. Atmosphere, 2017, 8(8): Article Number 136. |
| [54] | XIONG Z C, YANG R L, ZHU Y J, et al.Flexible hydroxyapatite ultralong nanowires-based paper for highly efficient and multifunctional air filtration.Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(33): 17482-17491. |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 安然, 林锶, 郭世刚, 张冲, 祝顺, 韩颖超. 铁掺杂纳米羟基磷灰石的制备及紫外吸收性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| [8] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [9] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [10] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [11] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [12] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [13] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [14] | 孙树娟, 郑南南, 潘昊坤, 马猛, 陈俊, 黄秀兵. 单原子催化剂制备方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [15] | 陶桂龙, 支国伟, 罗添友, 欧阳佩东, 衣新燕, 李国强. 空腔型薄膜体声波滤波器的关键技术进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||