无机材料学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 153-161.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170414 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20170414
聂恒昌1, 王永龄1, 贺红亮2, 王根水1, 董显林1
收稿日期:2017-08-25
修回日期:2017-11-13
出版日期:2018-02-26
网络出版日期:2018-01-26
作者简介:聂恒昌(1983),男,副研究员.E-mail:sestonenhc@mail.sic.ac.cn
基金资助:NIE Heng-Chang1, WANG Yong-Ling1, HE Hong-Liang2, WANG Gen-Shui1, DONG Xian-Lin1
Received:2017-08-25
Revised:2017-11-13
Published:2018-02-26
Online:2018-01-26
摘要:
基于铁电材料冲击波去极化效应的高功率脉冲电源在国防和高新技术领域具有重要应用。PZT95/5铁电陶瓷是目前铁电体高功率脉冲电源应用的理想材料。近年来, 多孔PZT95/5铁电陶瓷被发现具有更优异的综合性能而引起广泛关注。本文概述了多孔PZT95/5铁电陶瓷在微结构与性能调控、冲击波加载下的响应行为以及抗冲击损伤机制等方面的最新进展。研究发现, 具有合适气孔率和气孔分布的多孔PZT95/5铁电陶瓷具有优异的抗冲击损伤和耐电击穿性能; 多孔脆性材料中破碎介质的“滑移与转动”变形机制增强了材料的塑性变形, 从而提高了多孔材料的抗冲击损伤性能。最后, 简要介绍了BNT基无铅铁电陶瓷以及PIN-PMN铁电单晶在高功率脉冲电源方面应用的研究进展, 并对未来研究工作提出展望。
中图分类号:
聂恒昌, 王永龄, 贺红亮, 王根水, 董显林. 多孔PZT95/5铁电陶瓷材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(2): 153-161.
NIE Heng-Chang, WANG Yong-Ling, HE Hong-Liang, WANG Gen-Shui, DONG Xian-Lin. Recent Progress of Porous PZT95/5 Ferroelectric Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(2): 153-161.

图3 (a)糊精(Dextrin)和(b)聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA)及其作为造孔剂及制备的PZT95/5铁电陶瓷(c~d)的SEM照片[28-29]
Fig. 3 SEM images of (a) Dextrin, (b) PMMA, (c) PZT 95/5 ceramics with Dextrin as pore formers and (d) PZT 95/5 ceramics with PMMA as pore formers[28-29]

图4 不同微结构孔的多孔PZT95/5铁电陶瓷SEM照片[37]
Fig. 4 SEM images of the porous PZT95/5 ceramics with different pore sizes[37] (a) 1.8 mm PMMA spheres; (b) 5 μm PMMA spheres; (c) 15 μm PMMA spheres; (d) 60 μm PMMA spheres
| Property | Dense PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics | Porous PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk density/(g•cm-3) | ~7.6 | ~7.3 |
| Effective permittivity | 280-300 | 250-260 |
| Piezoelectric constant/(pC•N-1) | 66-70 | 66-70 |
| Bulk resistivity/(Ω•cm) | 1011-12 | 1011-12 |
| Tangent loss/% | 1.7-2.0 | 1.5-1.8 |
| Remnant polarization/(μC•cm-2) | ~35 | ~30 |
表1 气孔均匀分布的多孔PZT95/5铁电陶瓷与致密陶瓷性能比较[39-40]
Table 1 Physical property comparison between dense and porous PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics with disperse distribution[39-40]
| Property | Dense PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics | Porous PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk density/(g•cm-3) | ~7.6 | ~7.3 |
| Effective permittivity | 280-300 | 250-260 |
| Piezoelectric constant/(pC•N-1) | 66-70 | 66-70 |
| Bulk resistivity/(Ω•cm) | 1011-12 | 1011-12 |
| Tangent loss/% | 1.7-2.0 | 1.5-1.8 |
| Remnant polarization/(μC•cm-2) | ~35 | ~30 |
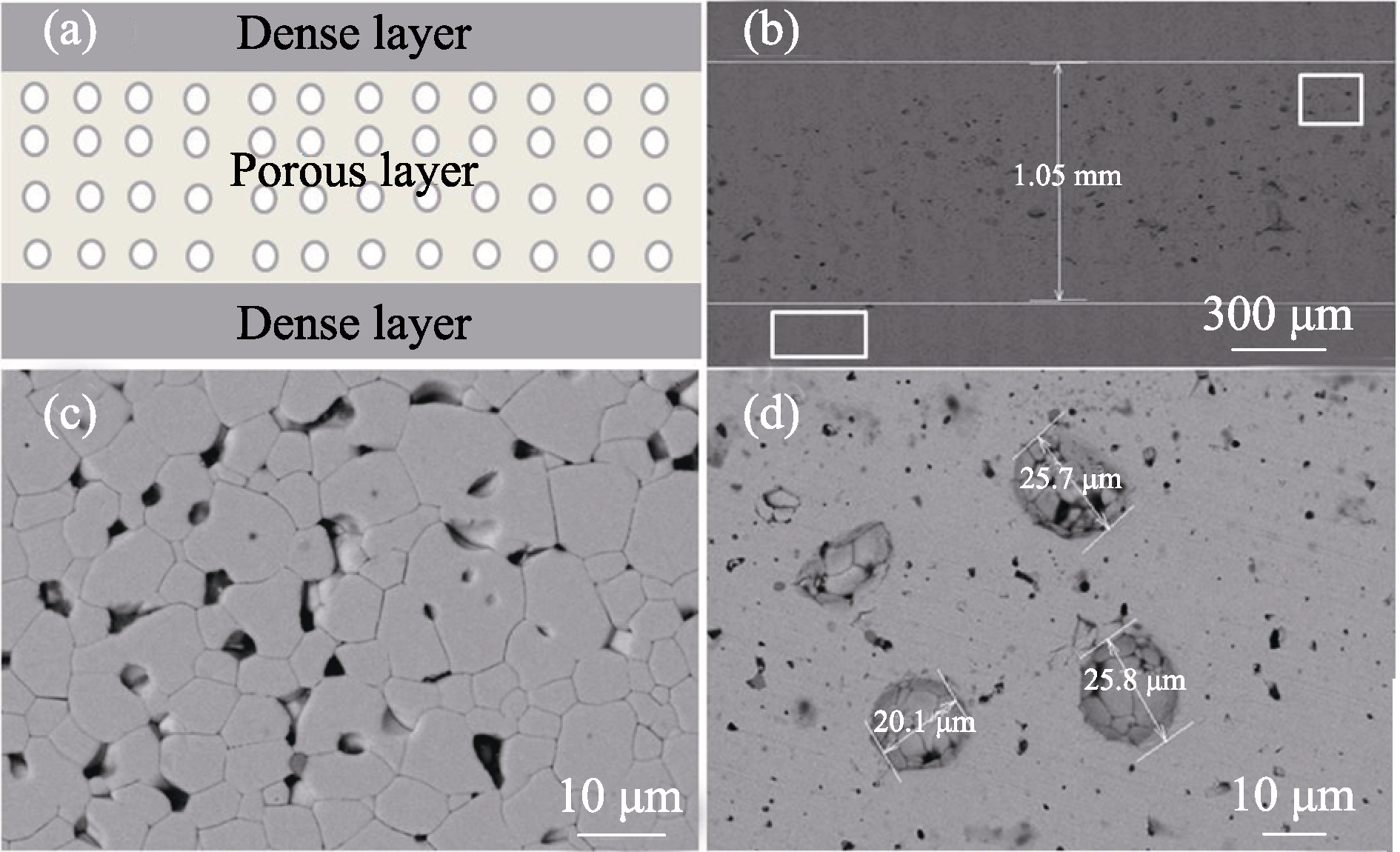
图7 (a)三明治结构的PZT95/5铁电陶瓷的断面结构示意图以及(b)断面、(c) 致密层和(d)多孔层的SEM照片[42]
Fig. 7 Schematic diagram (a) and SEM images of polished fracture cross section of sandwich structure PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramic: (b) full cross section; (c) dense layer; (d) porous layer[42]

图9 不同冲击压力下均匀分布气孔多孔PZT95/5铁电陶瓷动态响应行为[40]
Fig. 9 Dynamic response behaviors of porous PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics with disperse pores under different shock pressures[40]
| Catalogue | Property |
|---|---|
| Type I (not dependent on porosity) | Curie temperature, Spontaneous polarization |
| Type II (depend only on the amount of porosity) | Remnant polarization, bulk density, effective permittivity, piezoelectric constant, tangent loss, Young’s modulus, Dynamic yielding threshold |
| Type III (depend on both the amount and one or more characteristics of porosity) | Shock plasticity, Dielectric strength |
表2 多孔PZT95/5铁电陶瓷的性质与气孔的关系
Table 2 Relationship catalogue between physical property and pore of PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics
| Catalogue | Property |
|---|---|
| Type I (not dependent on porosity) | Curie temperature, Spontaneous polarization |
| Type II (depend only on the amount of porosity) | Remnant polarization, bulk density, effective permittivity, piezoelectric constant, tangent loss, Young’s modulus, Dynamic yielding threshold |
| Type III (depend on both the amount and one or more characteristics of porosity) | Shock plasticity, Dielectric strength |
| [1] | 钟维烈. 铁电体物理学. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998. |
| [2] | 王永龄. 功能陶瓷性能与应用. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003. |
| [3] | 贺元吉, 张亚洲, 李传胪. 爆电换能的理论分析. 国防科技大学学报, 2000, 22(z1): 43-48. |
| [4] | 刘高旻, 刘雨生, 张毅, 等. PZT铁电陶瓷及其在脉冲能源中的应用. 材料导报, 2006, 20(6): 74-77. |
| [5] | NEILSON F W.Effects of strong shocks in ferroelectric materials.Bull. Am. Phys. Soc., 1957, 2(2): 302. |
| [6] | BERLINCOURT D, JAFFE H, KRUEGER H H A, et al. Release of electric energy in PbNb(Zr,Ti,Sn)O3 by temperature-and by pressure-enforced phase transitions.Applied Physics Letters, 1963, 3(5): 90-92. |
| [7] | LYSNE P C, PERCIVAL C M.Electric energy generation by shock compression of ferroelectric ceramics: normal-mode response of PZT 95/5.Journal of Applied Physics, 1975, 46(4): 1519-1525. |
| [8] | STORZ L J, DUNGAN R H.A Study of the Electrical, Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of 95/5 PZT as Function of Pore Former Type and Concentration, Sandia Report, SAND85-1612[R]. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1985. |
| [9] | YONGLING W, WAN-ZONG Y, GUO-RONG H, et al.Study on shock wave-explosive energy converter of PZT 95/5 ferroelectric ceramics.Ferroelectrics, 1983, 49(1): 169-176. |
| [10] | FRITZ I J, KECK J D.Pressure-temperature phase diagrams for several modified lead zirconate ceramics.Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1978, 39(11): 1163-1167. |
| [11] | ALTGILBERS L L, BAIRD J, FREEMAN B, et al.Explosive Pulsed Power. London: Imperial College Press, 2010. |
| [12] | SHKURATOV S I, BAIRD J, ANTIPOV V G, et al.Depolarization mechanisms of PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 and PbZr0.95Ti0.05O3 poled ferroelectrics under high strain rate loading.Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(21): 212901. |
| [13] | SHKURATOV S I, BAIRD J, TALANTSEV E F.Note: utilizing Pb(Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 ferroelectric ceramics to scale down autonomous explosive-driven shock-wave ferroelectric generators.Review of Scientific Instruments, 2012, 83(7): 076104. |
| [14] | ALTGILBERS L L, STULTS A H, KRISTIANSEN M, et al.Recent advances in explosive pulsed power.Journal of Directed Energy, 2009, 3(2): 149-191. |
| [15] | VALADEZ J C, SAHUL R, ALBERTA E, et al.The effect of a hydrostatic pressure induced phase transformation on the unipolar electrical response of Nb modified 95/5 lead zirconate titanate.Journal of applied physics, 2012, 111(2): 024109. |
| [16] | JAFFE B, COOK W K, JAFFE H, et al.Piezoelectric ceramics. Academic Press, 1971. |
| [17] | LOCKWOOD STEVE, VOIGHT JIM, PIKE RICK, et al.PZT Supply Team Goes from Basic Research to WR Production. MFG S&T Quarterly, 2003, 11: 2. |
| [18] | DUNGAN R H, STORZ L J.Relation between chemical, mechanical, and electrical properties of Nb2O5-modified 95mol% PbZrO3-5mol% PbTiO3.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1985, 68(10): 530-533. |
| [19] | TUTTLE B, VOIGT J, MOORE R.Structure-property Relationships of Antiferroelectric Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 Based Materials: Hydrostatic Depoling Characteristics. Sandia National Labs., Albuquerque, NM(United States), 1997. |
| [20] | TUTTLE B A, YANG P, GIESKE J H, et al.Pressure-induced phase transformation of controlled-porosity Pb(Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 ceramics.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001, 84(6): 1260-1264. |
| [21] | SING K S W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (recommendations 1984).Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1985, 57(4): 603-619. |
| [22] | STUDART A R, GONZENBACH U T, TERVOORT E, et al.Processing routes to macroporous ceramics: a review.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(6): 1771-1789. |
| [23] | OHJI T, FUKUSHIMA M.Macro-porous ceramics: processing and properties.International Materials Reviews, 2012, 57(2): 115-131. |
| [24] | HAMMEL E C, IGHODARO O L R, OKOLI O I. Processing and properties of advanced porous ceramics: an application based review.Ceramics International, 2014, 40(10): 15351-15370. |
| [25] | 陈永. 多孔材料制备与表征. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2010. |
| [26] | YANG P, MOORE R H, LOCKWOOD S J BRUCE A, et al. Chem-prep PZT95/5 for Neutron Generator Applications: ehe Effect of Pore Former Type and Density on the Depoling Behavior of Chemically Prepared PZT 95/5 ceramics, Sandia Report SAND2003- 0537[R]. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2003. |
| [27] | SETCHELL R E, TUTTLE B A, VOIGT J A.Effects of Microstructural Variables on the Shock Wave Response of PZT 95/5. Sandia Report SAND2003-0537. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2003. |
| [28] | ZENG T, DONG X L, MAO C L, et al.Effects of pore shape and porosity on the properties of porous PZT 95/5 ceramics.Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2007, 27(4): 2025-2029. |
| [29] | ZENG T, WANG G, DONG X, et al.Investigation on FR(LT)-FR(HT) phase transition and pyroelectric properties of porous Zr-rich lead zirconate titante ceramics.Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2007, 140(1): 5-9. |
| [30] | NIE H C, DONG X L, FENG N B, et al.Quantitative dependence of the properties of Pb0.99(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3 ferroelectric ceramics on porosity.Materials Research Bulletin, 2010, 45(5): 564-567. |
| [31] | 王永刚. 多孔未极化 Pb(Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 铁电陶瓷单轴压缩力学响应与相变. 物理学报, 2015, 64: 134601. |
| [32] | 蒋招绣, 申海艇, 辛铭之, 等. 多孔极化PZT95/5 铁电陶瓷单轴压缩力学响应与放电特性. 固体力学学报, 2016, 37(1): 50-58. |
| [33] | SETCHELL R E.Shock wave compression of the ferroelectric ceramic Pb0.99(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3: Hugoniot states and constitutive mechanical properties.Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 94(1): 573-588. |
| [34] | SETCHELL R E.Shock wave compression of the ferroelectric ceramic Pb0.99(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3: depoling currents.Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 97(1): 013507. |
| [35] | SETCHELL R E.Shock wave compression of the ferroelectric ceramic Pb0.99(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3: microstructural effects. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 101(5): 053525. |
| [36] | FENG N, NIE H, CHEN X, et al.Depoling of porous Pb0.99(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3 ferroelectric ceramics under shock wave load.Current Applied Physics, 2010, 10(6): 1387-1390. |
| [37] | NIE H C, DONG X, FENG N, et al.Microgeometry effect on the properties of Pb0.99(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3 ferroelectric ceramics.Materials Research Bulletin, 2011, 46(8): 1243-1246. |
| [38] | NIE H C, FENG N B, CHEN X F, et al.Enhanced ferroelectric properties of intragranular-porous Pb (Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 ceramic fabricated with carbon nanotubes.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 93(3): 642-645. |
| [39] | NIE H C, DONG X, CHEN X, et al.Formation mechanism of intragranular pores in Pb(Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 ferroelectric ceramic.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(1): 223-226. |
| [40] | NIE H C, YU Y, LIU Y, et al. Enhanced shock performance by disperse porous structure: a case study in PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, DOI:10.1111/ jace.15097, 2017, 1-7. |
| [41] | MOORE R H, HUTCHINSON M A, MONTOYA T V, et al. Method of Making and Ceramic Articles with Multiple Regions of Distinct Density: U.S. Patent 8,212,456.2012-7-3. |
| [42] | NIE H C, DONG X, CHEN X, et al.Enhanced performances of sandwich structure Pb0.99 (Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98Nb0.02O3 ferroelectric ceramics for pulsed power application. Materials Research Bulletin, 2014, 51(9): 167-170. |
| [43] | LYSNE P C.Dielectric breakdown of shock-loaded PZT 65/35.Journal of Applied Physics, 1973, 44(2): 577-582. |
| [44] | LYSNE P C.Dielectric properties of shock-wave-compressed PZT 95/5.Journal of Applied Physics, 1977, 48(3): 1020-1023. |
| [45] | LYSNE P C.Resistivity of shock-wave-compressed PZT 95/5.Journal of Applied Physics, 1977, 48(11): 4565-4568. |
| [46] | CHHABILDAS L C.Dynamic Shock Studies of PZT 95/5 Ferroelectric Ceramic. Sandia Report, SAND84-1729. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1984. |
| [47] | CHHABILDAS L C, CARR M J, KUNZ S C, et al.Shock Recovery Experiments on PZT 95/5. Sandia Report, SAND85-0406C. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1985. |
| [48] | HALPIN W J.Resistivity estimates for some shocked ferroelectrics.Journal of Applied Physics, 1968, 39(8): 3821-3826. |
| [49] | TKACH Y, SHKURATOV S I, TALANTSEV E F, et al.Theoretical treatment of explosive-driven ferroelectric generators.IEEE Transactions On Plasma Science, 2002, 30(5): 1665-1673. |
| [50] | ZHANG F, HE H, LIU G, et al.Failure behavior of Pb (Zr0.95Ti0.05) O3 ferroelectric ceramics under shock compression.Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113(18): 183501. |
| [51] | ZHANG F, LIU Y, XIE Q, et al.Electrical response of Pb (Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 under shock compressions.Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 117(13): 134104. |
| [52] | NIE H C, YANG J, CHEN X, et al.Mechanical induced electrical failure of shock compressed PZT95/5 ferroelectric ceramics.Current Applied Physics, 2017, 17(4): 448-453. |
| [53] | 喻寅, 王文强, 杨佳, 等. 多孔脆性介质冲击波压缩破坏的细观机理和图像. 物理学报, 2012, 61(4): 48103. |
| [54] | YU Y, WANG W, HE H, et al.Mesoscopic deformation features of shocked porous ceramic: polycrystalline modeling and experimental observations.Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 117(12): 125901. |
| [55] | YU Y, WANG W, HE H, et al.Modeling multiscale evolution of numerous voids in shocked brittle material.Physical Review E, 2014, 89(4): 043309. |
| [56] | 喻寅, 贺红亮, 王文强, 等. 含微孔洞脆性材料的冲击响应特性与介观演化机制. 物理学报, 2014, 63(24): 246102. |
| [57] | 喻寅, 贺红亮, 王文强, 等. 多孔脆性材料对高能量密度脉冲的吸收和抵抗能力. 物理学报, 2015, 64(12): 124302. |
| [58] | JIANG T, YU Y, HE H, et al.Macroscopic shock plasticity of brittle material through designed void patterns.Journal of Applied Physics, 2016, 119(9): 095905. |
| [59] | RICE R W.The Porosity Dependence of Physical Properties of Materials: a Summary Review, Key Engineering Materials. Zürich Trans Tech Publications, 1996, 115: 1-20. |
| [60] | LIU Z, REN W, NIE H, et al.Pressure driven depolarization behavior of Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 based lead-free ceramics.Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110(21): 212901. |
| [61] | SHKURATOV S I, BAIRD J, ANTIPOV V G, et al.Ultrahigh energy density harvested from domain-engineered relaxor ferroelectric single crystals under high strain rate loading. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 46758. |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | 孙树娟, 郑南南, 潘昊坤, 马猛, 陈俊, 黄秀兵. 单原子催化剂制备方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | 陶桂龙, 支国伟, 罗添友, 欧阳佩东, 衣新燕, 李国强. 空腔型薄膜体声波滤波器的关键技术进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | 周帆, 田志林, 李斌. 热防护系统用碳化物超高温陶瓷抗烧蚀涂层研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||