无机材料学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 1-10.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160297 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20160297
• • 下一篇
罗 维1,2, 魏 晶3, 邓勇辉3, 李宇慧3, 王连军1, 赵 涛1, 江 莞1
收稿日期:2016-05-10
修回日期:2016-06-14
出版日期:2017-01-20
网络出版日期:2016-12-15
作者简介:罗 维(1983–), 男, 博士, 讲师. E-mail: wluo@dhu.edu.cn
基金资助:LUO Wei1,2, WEI Jing3, DENG Yong-Hui3, LI Yu-Hui3, WANG Lian-Jun1, ZHAO Tao1, JIANG Wan1
Received:2016-05-10
Revised:2016-06-14
Published:2017-01-20
Online:2016-12-15
About author:LUO Wei. E-mail: wluo@dhu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
自从1992年首次报道介孔氧化硅分子筛M41S系列以来, 人们采用各种商业化表面活性剂为模板, 合成了多种骨架组成、丰富的有序介观结构、不同孔径尺寸的介孔材料, 并将其应用在能源、环境、催化等诸多领域。然而, 由于常规商业化模板剂的分子量大小有限, 合成的介孔材料具有较小的孔径(< 8.0 nm), 从而极大地限制了其面对大尺寸客体分子的相关应用。此外, 利用常规模板剂难以合成出具有晶化墙壁的介孔金属氧化物材料。近年来, 大分子量两亲性嵌段共聚物相继被报道用来合成新型介孔材料, 本文将综述基于这种嵌段共聚物为模板剂合成各种具有大孔径和晶化墙壁介孔材料的研究进展。
中图分类号:
罗 维, 魏 晶, 邓勇辉, 李宇慧, 王连军, 赵 涛, 江 莞. 新型两亲性嵌段共聚物导向合成有序大孔径介孔材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(1): 1-10.
LUO Wei, WEI Jing DENG Yong-Hui, LI Yu-Hui, WANG Lian-Jun, ZHAO Tao, JIANG Wan. Progress on the Fabrication of Ordered Mesoporous Materials with Large Pores by Using Novel Amphiphilic Block Copolymers as Templates[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 1-10.
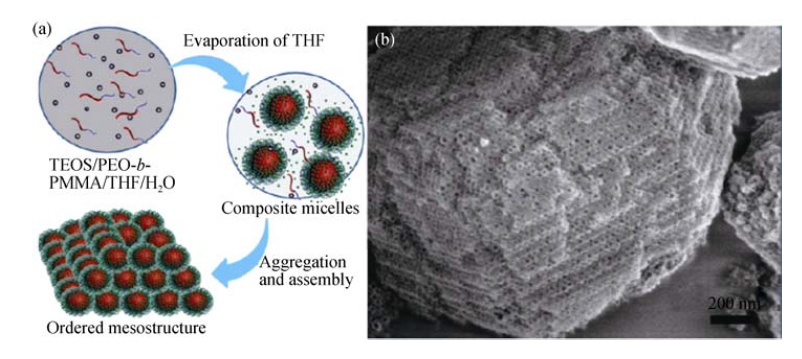
图2 EIAA法合成有序介孔氧化硅的机理示意图(a)和扫描电镜照片(b)[36]
Fig. 2 Schematic illustration of the formation process (a) and SEM image of mesoporous silica via EIAA approach (b)[36]
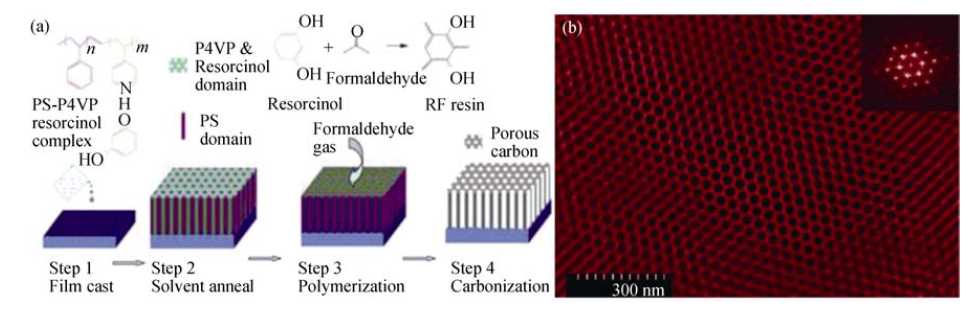
图3 以PS-b-P4VP为模板合成有序介孔碳材料的机理示意图(a)和扫描电镜照片(b)[43]
Fig. 3 Schematic illustration of the formation process of mesoporous carbon by using amphiphilic PS-b-P4VP copolymers as template (a) and its corresponding SEM image (b)[43]
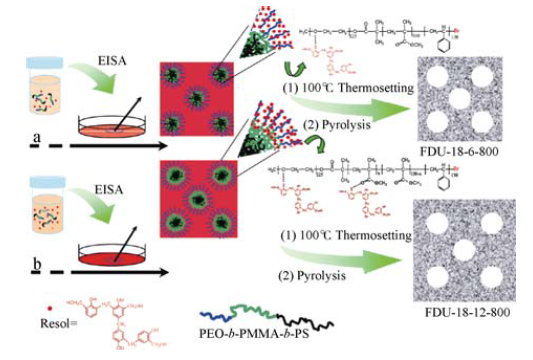
图4 PEO-b-PMMA-b-PS为模板剂合成孔径与墙壁厚度可调的有序介孔碳材料示意图[46]
Fig. 4 Schematic illustration of the formation process of mesoporous carbon with tunable pore size and wall thickness by using amphiphilic PEO-b-PMMA-b-PS copolymers as template[46]
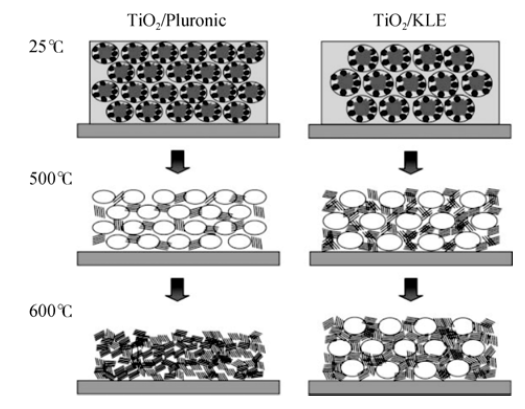
图5 选用KLE或P123为模板剂得到介孔二氧化钛材料的晶化过程示意图[50]
Fig. 5 Schematic illustration of the crystallization process of mesoporous titania by using KLE or P123 as templates[50]

图6 利用软-硬模板共组装(CASH)的方法合成高度晶化的介孔二氧化钛示意图[51]
Fig. 6 Schematic illustration of the formation process of mesoporous titania with high crystallinity via CASH approach[51]

图7 利用嵌段共聚物PEO-b-PS为模板剂合成具有简单立方介观结构的大孔径有序介孔氧化钛机理图[52]
Fig. 7 Schematic illustration of the formation process of mesoporous titania with large pores and simple cubic structure by using amphiphilic PEO-b-PS copolymers as template[52]
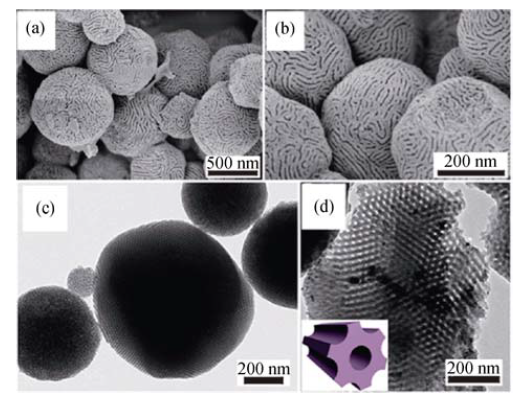

图8 以PEO-b-PS为模板剂通过RA-EISA法合成介孔氧化铌微球的场发射扫描电镜照片(a, b)和透射电镜照片(c, d)[18]
Fig. 8 SEM (a,b) and TEM (c,d) images of mesoporous niobia spheres via RA-EISA approach by using amphiphilic PEO-b-PS copolymers as template[18]
| [1] | SHI Y, WAN Y, ZHAO D.Ordered mesoporous non-oxide materials.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40(7): 3854-3878. |
| [2] | ZHAO D, FENG J,HUO Q, et al. Triblock copolymer syntheses of mesoporous silica with periodic 50 to 300 angstrom pores.Science, 1998, 279(5350): 548-552. |
| [3] | BECK J S, VARTULI J C,ROTH W J, et al. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, 114(27): 10834-10843. |
| [4] | MENG Y, GU D, ZHANG F, et al. A Family of highly ordered mesoporous polymer resin and carbon structures from organic-organic self-sssembly.Chem. Mater., 2006, 18(18): 4447-4464. |
| [5] | ZHAI Y, DOU Y, ZHAO D, et al. Carbon materials for chemical capacitive energy storage. Adv. Mater., 2011, 23(42): 4828-4850. |
| [6] | LIU Y, LAN K, BAGABAS A A, et al. Ordered macro/mesoporous TiO2 hollow microspheres with highly crystalline thin shells for high-efficiency photoconversion.Small, 2016, 12(7): 860-867. |
| [7] | WANG C, LI X, XI X, et al. Bimodal highly ordered mesostructure carbon with high activity for Br2/Br- redox couple in bromine based batteries.Nano Energy, 2016, 21: 217-227. |
| [8] | LIU H, LI W, SHEN D, et al. Graphitic carbon conformal coating of mesoporous TiO2 hollow spheres for high-performance lithium ion battery anodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(40): 13161-13166. |
| [9] | ZHOU W, GAO H,GOODENOUGH J B.Low-cost hollow mesoporous polymer spheres and all-solid-state lithium, sodium batteries.Adv. Energy Mater., 2016, 6(1):1501802. |
| [10] | DENG Y, CAI Y, SUN Z, et al. Multifunctional mesoporous composite microspheres with well-designed nanostructure: a highly integrated catalyst system.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(24): 8466-8473. |
| [11] | GARG S, SONI K, AJEETH PRABHU T, et al. Effect of ordered mesoporous Zr SBA-15 support on catalytic functionalities of hydrotreating catalysts 2.Variation of molybdenum and promoter loadings. Catal. Today, 2016, 261: 128-136. |
| [12] | DUTTA B, BISWAS S, SHARMA V, et al. Mesoporous manganese oxide catalyzed aerobic oxidative coupling of anilines to aromatic azo compounds.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(6): 2171-2175. |
| [13] | JOO S H, PARK J Y, TSUNG C K, et al. Thermally stable Pt/mesoporous silica core-shell nanocatalysts for high-temperature reactions. Nat. Mater., 2009, 8(2): 126-131. |
| [14] | EGODAWATTE S, DATT A, BURNS E A, et al. Chemical insight into the adsorption of chromium(III) on iron oxide/mesoporous silica nanocomposites.Langmuir, 2015, 31(27): 7553-7562. |
| [15] | FAN J, YU C, GAO F,, et al. Cubic mesoporous silica with large controllable entrance sizes and advanced adsorption properties.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2003, 42(27): 3146-3150. |
| [16] | TENG W, WU Z, FAN J, et al. Amino-functionalized ordered mesoporous carbon for the separation of toxic microcystin-LR. J. Mater. Chem., 2015, 3(37): 19168-19176. |
| [17] | WU C, LIANG Y, YANG K, et al. Clickable periodic mesoporous organosilica monolith for highly efficient capillary chromatographic separation. Anal. Chem., 2016, 88(3): 1521-1525. |
| [18] | LUO W, LI Y, DONG J, et al. A resol-assisted co-assembly approach to crystalline mesoporous niobia spheres for electrochemical biosensing.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(40): 10505-10510. |
| [19] | GE X, SUN L, MA B, et al. Simultaneous realization of Hg2+ sensing, magnetic resonance imaging and upconversion luminescence in vitro and in vivo bioimaging based on hollow mesoporous silica coated UCNPs and ruthenium complex. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(33): 13877-13887. |
| [20] | LI Z, CLEMENS D L,LEE B Y, et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles with pH-sensitive nanovalves for delivery of moxifloxacin provide improved treatment of lethal pneumonic tularemia.ACS Nano, 2015, 9(11): 10778-10789. |
| [21] | LIU J, LUO Z, ZHANG J, et al. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles facilitated drug delivery via cascade pH stimuli in tumor microenvironment for tumor therapy.Biomaterials, 2016, 83: 51-65. |
| [22] | WANG Y, GU H.Core shell-type magnetic mesoporous silica nanocomposites for bioimaging and therapeutic agent delivery.Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(3): 576-585. |
| [23] | SCHÜTH F. Non-siliceous mesostructured and mesoporous materials.Chem. Mater., 2001, 13(10): 3184-3195. |
| [24] | WIDENMEYER M,ANWANDER R.Pore size control of highly ordered mesoporous silica MCM-48.Chem. Mater., 2002, 14(4): 1827-1831. |
| [25] | YU C, FAN J, TIAN B, et al. Synthesis of mesoporous silica from commercial poly(ethylene oxide)/poly(butylene oxide) copolymers: toward the rational design of ordered mesoporous materials. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2003, 107(48): 13368-13375. |
| [26] | HUO Q, MARGOLESE D I,STUCKY G D.Surfactant control of phases in the synthesis of mesoporous silica-based materials.Chem. Mater., 1996, 8(5): 1147-1160. |
| [27] | KRESGE C T, LEONOWICZ M E, ROTH W J, et al. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature, 1992, 359(6397): 710-712. |
| [28] | GAO C, SAKAMOTO Y, SAKAMOTO K, et al. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous silica AMS-10 with bicontinuous cubic Pn3m symmetry.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2006, 45(26): 4295-4298. |
| [29] | CHE S, GARCIA-BENNETT A E, YOKOI T, et al. A novel anionic surfactant templating route for synthesizing mesoporous silica with unique structure.Nat. Mater., 2003, 2(12): 801-805. |
| [30] | GARCIA-BENNETT A E, KUPFERSCHMIDT N, SAKAMOTO Y, et al. Synthesis of mesocage structures by kinetic control of self-assembly in anionic surfactants. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 44(33): 5317-5322. |
| [31] | ZHAO D, HUO Q, FENG J, et al. Nonionic triblock and star diblock copolymer and oligomeric surfactant syntheses of highly ordered, hydrothermally stable, mesoporous silica structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1998, 120(24): 6024-6036. |
| [32] | FAN J, YU C, LEI J, et al. Low-temperature strategy to synthesize highly ordered mesoporous silicas with very large pores. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(31): 10794-10795. |
| [33] | MA G, YAN X, LI Y, et al. Ordered nanoporous silica with periodic 30-60 nm pores as an effective support for gold nanoparticle catalysts with enhanced lifetime.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(28): 9596-9597. |
| [34] | BRINKER C J, LU Y, SELLINGER A, et al. Evaporation-induced self-assembly: nanostructures made easy. Adv. Mater., 1999, 11(7): 579-585. |
| [35] | DENG Y, CAI Y, SUN Z, et al. Controlled synthesis and functionalization of ordered large-pore mesoporous carbons. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2010, 20(21): 3658-3665. |
| [36] | WEI J, WANG H, DENG Y, et al. Solvent evaporation induced aggregating assembly approach to three-dimensional ordered mesoporous silica with ultralarge accessible mesopores. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(50): 20369-20377. |
| [37] | WEI J, YUE Q, SUN Z, et al. Synthesis of dual-mesoporous silica using non-ionic diblock copolymer and cationic surfactant as co-templates.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 51(25): 6149-6153. |
| [38] | WANG C, WEI J, YUE Q, et al. A shear stress regulated assembly route to silica nanotubes and their closely packed hollow mesostructures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(44): 11603-11606. |
| [39] | YU K, SMARSLY B, BRINKER C J.Self-Assembly and characterization of mesostructured silica films with a 3D arrangement of isolated spherical mesopores.Adv. Funct. Mater., 2003, 13(1): 47-52. |
| [40] | SMARSLY B, XOMERITAKIS G,YU K, et al. Microstructural characterization of polystyrene-block-poly(ethylene oxide)-templated silica films with cubic-ordered spherical mesopores. Langmuir, 2003, 19(18): 7295-7301. |
| [41] | YU K, HURD A J, EISENBERG A, et al. Syntheses of silica/ polystyrene-block-poly (ethylene oxide) films with regular and reverse mesostructures of large characteristic length scales by solvent evaporation-induced self-assembly. Langmuir, 2001, 17(26): 7961-7965. |
| [42] | DENG Y, YU T, WAN Y, et al. Ordered mesoporous silicas and carbons with large accessible pores templated from amphiphilic diblock copolymer poly(ethylene oxide)-b-polystyrene. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129(6): 1690-1697. |
| [43] | LIANG C, HONG K, GUIOCHON G A, et al. Synthesis of a large-scale highly ordered porous carbon film by self-assembly of block copolymers.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2004, 43(43): 5785-5789. |
| [44] | RODRIGUEZ A T, LI X, WANG J, et al. Facile synthesis of nanostructured carbon through self-assembly between block copolymers and carbohydrates. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2007, 17(15): 2710-2716. |
| [45] | DENG Y, LIU C, GU D, et al. Thick wall mesoporous carbons with a large pore structure templated from a weakly hydrophobic PEO-PMMA diblock copolymer. J. Mater. Chem., 2008, 18(1): 91-97. |
| [46] | ZHANG J, DENG Y, WEI J, et al. Design of amphiphilic ABC triblock copolymer for templating synthesis of large-pore ordered mesoporous carbons with tunable pore wall thickness. Chem. Mater., 2009, 21(17): 3996-4005. |
| [47] | WEI J, DENG Y,ZHANG J, et al. Large-pore ordered mesoporous carbons with tunable structures and pore sizes templated from poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(methyl methacrylate). Solid State Sci., 2011, 13(4): 784-792. |
| [48] | SMARSLY B, GROSSO D, BREZESINSKI T, et al. Highly crystalline cubic mesoporous TiO2 with 10-nm pore diameter made with a new block copolymer template. Chem. Mater., 2004, 16(15): 2948-2952. |
| [49] | BREZESINSKI T, GROENEWOLT M, GIBAUD A, et al. Evaporation-induced self-assembly (EISA) at its limit: ultrathin, crystalline patterns by templating of micellar monolayers. Adv. Mater., 2006, 18(17): 2260-2263. |
| [50] | FATTAKHOVA-ROHLFING D, WARK M, BREZESINSKI T, et al. Highly organized Mesoporous TiO2 films with controlled crystallinity: A Li-insertion study. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2007, 17(1): 123-132. |
| [51] | LEE J, CHRISTOPHER ORILALL M, WARREN S C, et al. Direct access to thermally stable and highly crystalline mesoporous transition-metal oxides with uniform pores. Nat. Mater., 2008, 7(3): 222-228. |
| [52] | ZHANG J, DENG Y, GU D, et al. Ligand-assisted assemblyapproach to synthesize large-pore ordered mesoporous titania with thermally stable and crystalline Framework. Adv. Energy Mater., 2011, 1(2): 241-248. |
| [53] | KUEMMEL M, GROSSO D,BOISSIRE C, et al. Thermally stable nanocrystalline γ-alumina layers with highly ordered 3D mesoporosity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 44(29): 4589-4592. |
| [54] | BREZESINSKI T, FATTAKHOVAβROHLFING D, SALLARD S, et al. Highly crystalline WO3 thin films with ordered 3D mesoporosity and improved electrochromic performance. Small, 2006, 2(10): 1203-1211. |
| [55] | LI Y, LUO W, QIN N, et al. Highly ordered mesoporous tungsten oxides with a large pore size and crystalline framework for H2S sensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(34): 9035-9040. |
| [56] | PARK T, AHN S, ROH D, et al. Multifunctional organized mesoporous tin oxide films templated by graft copolymers for dye-Sensitized solar cells. ChemSusChem, 2014, 7(7): 2037-2047. |
| [57] | BREZESINSKI T, WANG J,SENTER R, et al. On the correlation between mechanical flexibility, nanoscale structure, and charge storage in periodic mesoporous CeO2 thin films. ACS Nano, 2010, 4(2): 967-977. |
| [58] | BREZESINSKI T, ANTONIETTI M, GROENEWOLT M, et al. The generation of mesostructured crystalline CeO2, ZrO2 and CeO2-ZrO2 films using evaporation-induced self-assembly. New J. Chem., 2005, 29(1): 237-242. |
| [59] | FANG H, WAN T, SHI W, et al. Design and synthesis of large-pore p6mm mesoporus zirconia thin films templated by a novel block copolymer. J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2007, 353(16/17): 1657-1661. |
| [60] | ORTEL E, REIER T, STRASSER P, et al. Mesoporous IrO2 films templated by PEO-PB-PEO block-copolymers: self-assembly, crystallization behavior, and electrocatalytic performance. Chem. Mater., 2011, 23(13): 3201-3209. |
| [61] | YAMAUCHI Y, SUGIYAMA A, MORIMOTO R, et al. Mesoporous platinum with giant mesocages templated from lyotropic liquid crystals consisting of diblock copolymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2008, 47(29): 5371-5373. |
| [62] | TAKAI A, YAMAUCHI Y, KURODA K.Tailored electrochemical synthesis of 2D-hexagonal, lamellar, and cage-type mesostructured Pt thin films with extralarge periodicity.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(1): 208-214. |
| [63] | LIN Y, DAGA V K, ANDERSON E R, et al. Nanoparticle-driven assembly of clock copolymers: a simple route to ordered hybrid materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(17): 6513-6516. |
| [64] | HSUEH H Y, HUANG Y C, HO R M, et al. Nanoporous gyroid nickel from block copolymer templates via electroless plating. Adv. Mater., 2011, 23(27): 3041-3046. |
| [1] | 魏相霞, 张晓飞, 徐凯龙, 陈张伟. 增材制造柔性压电材料的现状与展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 965-978. |
| [2] | 杨鑫, 韩春秋, 曹玥晗, 贺桢, 周莹. 金属氧化物电催化硝酸盐还原合成氨研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 979-991. |
| [3] | 刘鹏东, 王桢, 刘永锋, 温广武. 硅泥在锂离子电池中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 992-1004. |
| [4] | 黄洁, 汪刘应, 王滨, 刘顾, 王伟超, 葛超群. 基于微纳结构设计的电磁性能调控研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 853-870. |
| [5] | 陈乾, 苏海军, 姜浩, 申仲琳, 余明辉, 张卓. 超高温氧化物陶瓷激光增材制造及组织性能调控研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 741-753. |
| [6] | 王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [7] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [8] | 吴晓晨, 郑瑞晓, 李露, 马浩林, 赵培航, 马朝利. SiCf/SiC陶瓷基复合材料高温环境损伤原位监测研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 609-622. |
| [9] | 赵日达, 汤素芳. 多孔碳陶瓷化改进反应熔渗法制备陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 623-633. |
| [10] | 方光武, 谢浩元, 张华军, 高希光, 宋迎东. CMC-EBC损伤耦合机理及一体化设计研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 647-661. |
| [11] | 张幸红, 王义铭, 程源, 董顺, 胡平. 超高温陶瓷复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 571-590. |
| [12] | 张慧, 许志鹏, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英. 大面积有机-无机杂化钙钛矿薄膜及其光伏应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 457-466. |
| [13] | 李宗晓, 胡令祥, 王敬蕊, 诸葛飞. 氧化物神经元器件及其神经网络应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 345-358. |
| [14] | 鲍可, 李西军. 化学气相沉积法制备智能窗用热致变色VO2薄膜的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 233-258. |
| [15] | 胡梦菲, 黄丽萍, 李贺, 张国军, 吴厚政. 锂/钠离子电池硬碳负极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 32-44. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||