无机材料学报 ›› 2013, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (2): 123-130.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2013.12127 CSTR: 32189.14.SP.J.1077.2013.12127
• • 下一篇
杜 刚, 梁瑞虹, 李 涛, 卢晓蓉, 王根水, 董显林
收稿日期:2012-03-01
修回日期:2012-05-23
出版日期:2013-02-10
网络出版日期:2013-01-23
作者简介:杜 刚(1987–), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: dugang0623@163.com
基金资助:DU Gang, LIANG Rui-Hong, LI Tao, LU Xiao-Rong, WANG Gen-Shui, DONG Xian-Lin
Received:2012-03-01
Revised:2012-05-23
Published:2013-02-10
Online:2013-01-23
About author:DU Gang. E-mail: dugang0623@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
压电材料通过受主掺杂或烧结挥发等可以形成缺陷偶极子, 缺陷偶极子对材料的性能有显著的影响。本文综述了压电材料中缺陷偶极子的产生及其在外场下的响应机理, 同时, 从缺陷偶极子运动的角度分析了压电材料中老化、电滞回线异常及电致形状记忆效应等现象的起源, 简要分析了偶极子弛豫现象, 并对未来发展高可靠性压电驱动器的研究作了展望。
中图分类号:
杜 刚, 梁瑞虹, 李 涛, 卢晓蓉, 王根水, 董显林. 压电材料中缺陷偶极子特性的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(2): 123-130.
DU Gang, LIANG Rui-Hong, LI Tao, LU Xiao-Rong, WANG Gen-Shui, DONG Xian-Lin. Recent Progress on Defect Dipoles Characteristics in Piezoelectric Materials[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(2): 123-130.

图2 (a)BaTi0.98Ca0.02O2.98陶瓷压电常数d33的老化曲线[30], (b)Ba(Ti1-xFex)O3陶瓷介电常数及损耗的老化曲线[29]
Fig. 2 (a) Aging of the piezoelectric coefficient for BaTi0.98Ca0.02O2.98 ceramic after poling[30]; (b) Aging of the dielectric constant and the dielectric loss for Ba(Ti1-xFex)O3 ceramics[29]

图3 含有缺陷偶极子的压电陶瓷极化老化后的(a)电滞回线, (b)极化反转电流-电场曲线, (c)电畴反转示意图(图中P是自发极化, Ei是内偏场)[18]
Fig. 3 Schematic representation of (a) asymmetric polarization hysteresis curve (b) I-E curve (c) domain switching of aged piezoelectric ceramics containing defect dipoles (P denotes spontaneous polarization, Ei denotes internal bias field) [18]

图4 (a)[001]取向PMNT62/38-0.2Fe单晶[7]和(b)PNZTM95/5陶瓷的束腰电滞回线[7,34]
Fig. 4 Constricted double hysteresis loops of (a) [001] oriented PMNT62/38-0.2Fe crystals[7] and (b) PNZTM95/5 ceramics[7,34]

图7 电致形状记忆效应机理示意图: (a)老化后的多畴四方铁电相, (b)施加电场后的单畴结构, (c)可逆畴变产生的双电滞回线, (d)大的可回复电致应变[37]
Fig. 7 Mechanism of large electro-shape-memory by reversible domain switching in aged ferroelectrics (a) multidomain tetragonal ferroelectrics after aging (b) single-domain state by electric field E (c) double hysteresis loop (P-E curve) during reversible domain switching (d) huge electrostrain (ε-E curve) during reversible domain switching[37]

图8 老化的[001]取向BaTiO3单晶及PZN-PT单晶、PZT陶瓷的电致形变的对比示意图[13]
Fig. 8 Large electric-field-induced strain in an aged [001]- oriented BaTiO3 single crystal in comparison with the piezoelectric effect of PZT ceramics and PZN-PT single crystals[13]
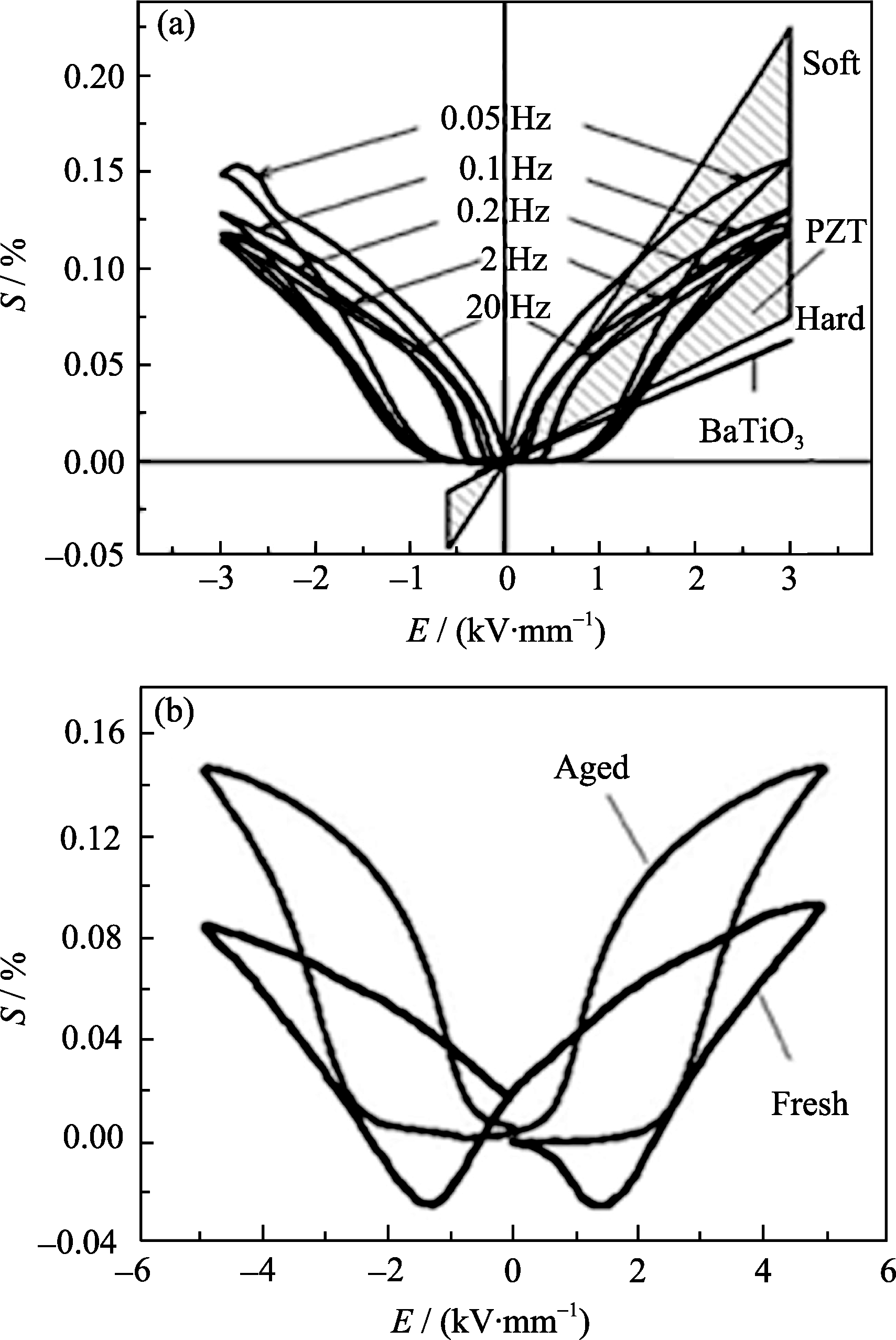
图9 (a) Mn掺杂Ba0.95Sr0.05TiO3陶瓷的电致形状记忆效应与BaTiO3 及PZT的线性压电效应对比, (b) Mn掺杂的 KNbO3基压电陶瓷老化前后的电致应变[11,14]
Fig. 9 (a) Comparison of the nonlinear recoverable electrostrain in Ba0.95Sr0.05TiO3-1Mn ceramics with linear piezoelectric strain of BaTiO3 and PZT ceramics and (b) bipolar electrostrain curves for the aged and fresh Mn-doped KNbO3 based piezoelectric ceramics[11,14]
| [1] | Elissalde C, Ravez J. Ferroelectric ceramics: defects and dielectric relaxations. J. Mater. Chem., 2001, 11(8): 1957-1967. |
| [2] | Haertling G H. Ferroelectric ceramics: history and technology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1999, 82(4): 797-818. |
| [3] | Damjanovic D. Ferroelectric, dielectric and piezoel-ectric properties of ferroelectric thin films and ceramics. Rep. Prog. Phys., 1998, 61(9): 1267-1324. |
| [4] | LIU Bai-Nian, MA Ying, ZHOU Yi-Chun. Molecular dynamics simulation of the strain-polarization coupling in BaTiO3 ferroelectrics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(12): 1247-1251. |
| [5] | Kamel T M. Poling of hard ferroelectric PZT ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 28(9): 1827-1838. |
| [6] | Lupascu D C, Genenko Y A, Balke N. Aging in ferroelectrics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2006, 89(1): 224-229. |
| [7] | Feng Z, Tan O, Zhu W, et al. Aging-induced giant recoverable electrostrain in Fe-doped 0.62Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.38PbTiO3 single crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. , 2008, 92(14): 142910-1-3. |
| [8] | YANG Gang, YUE Zhen-Xing, LI Long-Tu. Research progress on the characteristics and mechanism of applied field-induced fatigue in piezoelectric ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(1): 1-6. |
| [9] | Zhang L X, Ren X B. Aging behavior in single-domain Mn-doped BaTiO3 crystals: implication for a unified microscopic explanation of ferroelectric aging. Phys. Rev. B, 2006, 73(9): 094121-1-6. |
| [10] | Feng Z, Ren X. Aging effect and large recoverable electrostrain in Mn-doped KNbO3-based ferroelectrics. Appl. Phys. Lett. , 2007, 91(3): 032904-1-3. |
| [11] | Feng Z, Or S W. Aging-induced, defect-mediated double ferroelectric hysteresis loops and large recoverable electrostrains in Mn-doped orthorhombic KNbO3-based ceramics. J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 480(2): L29-L32. |
| [12] | Zhang L X, Ren X B. In situ observation of reversible domain switching in aged Mn-doped BaTiO3 single crystals. Phys. Rev. B, 2005, 71(17): 174108-1-8. |
| [13] | Ren X B. Large electric-field-induced strain in ferroelectric crystals by point-defect-mediated reversible domain switching. Nat. Mater., 2004, 3(2): 91-94. |
| [14] | Zhang L X, Chen W, Ren X B. Large recoverable electrostrain in Mn-doped (Ba, Sr)TiO3 ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 85(23): 5658-5660. |
| [15] | Li B S, Li G R, Yin Q R, et al. Pinning and depinning mechanism of defect dipoles in PMnN-PZT ceramics. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2005, 38(8): 1107-1111. |
| [16] | Feng Z, Ren X B. Striking similarity of ferroelectric aging effect in tetragonal, orthorhombic and rhombohedral crystal structures. Phys. Rev. B, 2008, 77(13): 134115-1-6. |
| [17] | Ren X B, Otsuka K. Universal symmetry property of point defects in crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2000, 85(5): 1016-1019. |
| [18] | Takahashi S. Effects of impurity doping in lead zirconate-titanate ceramics. Ferroelectrics, 1982, 41(1): 143-156. |
| [19] | Carl K, Hardtl K. Electrical after-effects in Pb(Ti, Zr)O3 ceramics. Ferroelectrics, 1978, 17(1): 473-486. |
| [20] | HE Lian-Xing, LI Cheng-En. Effects of manganese addition on piezoelectric properties of “Hard” lead zirconate titanate. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2000, 15(2): 293-298. |
| [21] | Eichel R A. Characterization of defect structure in acceptor-modified piezoelectric ceramics by multifrequency and multipulse electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 91(3): 691-701. |
| [22] | HOU Yu-Dong, YANG Zu-Pei, GAO Feng, et al. Effects of manganese addition on piezoelectric properties of 0.2PZN-0.8PZT ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2003, 18(3): 590-594. |
| [23] | LI Qi-Shou, XIAO Ding-Quan, ZHU Jian-Guo. Effect of Y-doping on the ferroelectric properties of BSPT high-temperature piezoelectric ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 25(2): 185-190. |
| [24] | Li B S, Li G R, Zhao S C, et al. Reorientation of defect dipoles in ferroelectric ceramics. Chin.Phys.Lett. , 2005, 22(5): 1236-1-3. |
| [25] | Eichel R A. Defect structure of oxide ferroelectrics—valence state, site of incorporation, mechanisms of charge compensation and internal bias fields. J. Electroceram., 2007, 19(1): 11-23. |
| [26] | Teranishi S, Suzuki M, Noguchi Y, et al. Giant strain in lead-free (Bi0. 5Na0. 5)TiO3-based single crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. , 2008, 92(18): 182905-1-3. |
| [27] | Schulze W A, Ogino K. Review of literature on aging of dielectrics. Ferroelectrics, 1988, 87(1): 361-377. |
| [28] | Sun D, Ren X, Otsuka K B. Stabilization effect in ferroelectric materials during aging in ferroelectric state. Appl. Phys. Lett. , 2005, 87(14): 142903-1-3. |
| [29] | Dechakupt T, Tangsritrakul J, Unruan M, et al. Electrical and aging properties of doped barium titanate ceramics. Ferroelectrics, 2010, 403(1): 97-103. |
| [30] | Zhang L, Ben L, Thakur O P, et al. Ferroelectric aging and recoverable electrostrain in BaTi0.98Ca0.02O2.98 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram.Soc., 2008, 91(9): 3101-3104. |
| [31] | Liu W, Chen W, Yang L, et al. Ferroelectric aging effect in hybrid-doped BaTiO3 ceramics and the associated large recoverable electrostrain. Appl. Phys. Lett. , 2006, 89(17): 172908-1-3. |
| [32] | Gao Y K, Uchino K, Viehland D. Effects of thermal and electrical histories on hard piezoelectrics: a comparison of internal dipolar fields and external dc bias. J. Appl. Phys. , 2007, 101(5): 054109-1-6. |
| [33] | Arlt G, Neumann H. Internal bias in ferroelectric ceramics: origin and time dependence. Ferroelectrics, 1988, 87(1): 109-120. |
| [34] | Jiang M, Li X, Zhu J, et al. Double hysteresis loops induced by Mn doping in Pb0.99Nb0.02(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98O3 ferroelectric ceramics. Curr. Appl. Phys., 2010, 10(2): 526-530. |
| [35] | Li B S, Zhu Z G, Li G R, et al. Peculiar hysteresis loop of Pb(Mn1/3Nb2/3)O3-Pb(Ti, Zr)O3 ceramics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2004, 43(4A): 1458-1463. |
| [36] | Tan Q, Li J, Viehland D. Role of lower valent substituent-oxygen vacancy complexes in polarization pinning in potassium-modified lead zirconate titanate. Appl. Phys. Lett., 1999, 75(3): 418-420. |
| [37] | Ren X B, Zhang L X. Electro-shape-memory effect in ferroelectric martensite. Mat. Sci. Eng.: A, 2006, 438: 1071-1076. |
| [38] | Liu W, Chen W, Yang L, et al. Electro-shape-memory effect in hybrid doped BaTiO3 ceramics. Mat. Sci. Eng.: A, 2006, 438-440: 350-353. |
| [39] | Gao Y, Uchino K, Viehland D. Domain wall release in "hard" piezoelectric under continuous large amplitude ac excitation. J. Appl. Phys. , 2007, 101(11): 114110-1-7. |
| [40] | Li Bao-Shan, Zhu Zhi-Gang, Li Guo-Rong, et al. Frequency and temperature dependence of the hysteresis loop in PMnN-PZT ceramics. Acta Physica Sinica, 2005, 54(2): 939-943 |
| [41] | Cao Z, Ding A, Zhang Y, et al. Double-hysteresis-like loops in Mn-doped (Pb, La)(Zr, Ti)O3 ceramics. Solid State Commun., 2004, 131(1): 57-60. |
| [42] | Lin D, Kwok K, Chan H. Double hysteresis loop in Cu-doped K0.5Na0.5NbO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. , 2007, 90(23): 232903-1-3. |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 孙雨萱, 王政, 时雪, 史颖, 杜文通, 满振勇, 郑嘹赢, 李国荣. 缺陷偶极子热稳定性对Fe掺杂PZT陶瓷机电性能影响研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 545-551. |
| [8] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [9] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [10] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [11] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [12] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [13] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [14] | 孙树娟, 郑南南, 潘昊坤, 马猛, 陈俊, 黄秀兵. 单原子催化剂制备方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [15] | 陶桂龙, 支国伟, 罗添友, 欧阳佩东, 衣新燕, 李国强. 空腔型薄膜体声波滤波器的关键技术进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||